Diamond like coatings (DLC) are today one of the most often used coatings for improvement of mechanical frictional and tribological performance of many components and parts1,2. The diamond like carbon term comprises different types of coatings or films whose structure is formed by amorphous carbon.
The main types of DLCs are
- hydrogen free diamond like carbon (commonly referred to as a-C),
- tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C),
- hydrogenated tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C:H).
Included as DLC coatings are also amorphous carbon films that contain small amounts of dopants such as metals. The DLC coatings are usually deposited either by Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or by Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), in some cases with plasma enhancement (PECVD). The typical thickness of the DLC films is in the range of several micrometers although some DLC films can be as thin as several tens of nanometers3.
This application report summarizes the use of indentation, scratch, tribology and coating thickness measurements for a complete characterization of mechanical properties, adhesion and thickness of DLC coatings.
Hardness and Elastic Modulus: Indentation
The Anton Paar Table Top Nanoindentation Tester (TTX-NHT3) has been developed for testing hard thin films such as TiN, AlTiN, CrN or DLC. The TTX-NHT3 is an excellent tool for both research and quality control to characterize hardness and elastic modulus of DLC films. Besides hardness and elastic modulus, the TTX-NHT3 can also calculate elastic and plastic work. All these results are automatically calculated according to the ISO 14577 standard. Figure 1 shows indentation load-indentation depth curves obtained on sample with 2 μm thick DLC coating deposited on metallic substrate using the TTX-NHT3.
Recommended test parameters:
- TTX-NHT3 (force range 0.1 to 500 mN)
- Berkovich indenter
- Fmax 2 mN to 100 mN
- Loading rate 4 to 200 mN/min
- Hold at Fmax: 5 s
The great advantage of the top reference in the NHT3 is not only its superior thermal stability but also the protection of the diamond indenter against damage. The NHT3 is therefore perfectly suitable for routine measurements in quality control or for university courses.
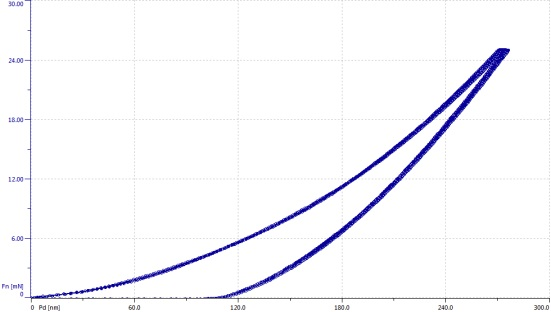
Figure 1. Typical indentation curves on 2 μm thick DLC coating (maximum load 25 mN, Berkovich indenter).
The indentation parameters have to be adjusted according to the thickness of the coating, surface roughness and hardness of the coating. It is recommended that the indentation depth should not exceed 10 % of the thickness of the coating (more detailed analysis of indentation conditions can be provided using our partner’s software). At the same time, the indentation depth should be at least 20 times higher than the surface roughness (Ra). In practice, a compromise is sometimes necessary; higher scatter of data has to be compensated for by larger number of automatic measurements in a matrix.

 Want to know more? Click here to read the full article.
Want to know more? Click here to read the full article.
.jpg)
This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Anton Paar GmbH.
For more information on this source, please visit Anton Paar GmbH.