Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), a Molecular Weight Determination with the BI-MwA
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is a polar molecule and is employed in a broad range of applications. For instance, as it easily passes through humans, it is used as a binding agent in pharmaceutical tablets. As PVP binds to polar molecules reasonably well, it is additionally employed as a paper coating. PVP is also present in toothpaste, paint shampoo and adhesives.
Fast, dependable characterization is critical for better comprehension of manufacturing execution, processing and structure-property relations. With the appropriate selection of instruments, the determination of molecular weight of PVP is simple.

Image Credit: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation
In water, PVP found in Aldrich was dissolved i and data was gathered with a BI-MwA in batch mode. A substantial issue in light scattering is dust and the BI-MwA design offers an answer with its sealed flow system and automatic dust elimination algorithms. These elements remove the deleterious impacts of dust.
Image Credit: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation
Employing the BI-MwA software, values for Kc/∆R were automatically calculated. Here, K is the Debye constant and it is proportional to the square of the refractive index increment, dn/dc. A value of 0.174 mL/g is employed for dn/dc. c is polymer concentration and ∆R is relative to the surplus scattered strength.
To establish molecular weight, the software then produces a Zimm, Berry, or Debye plot and values for molecular weight, radius of gyration (apart from in the instance of a Debye plot) and second virial coefficient are determined and shown. Following extrapolation to zero angle and zero concentration, the amount Kc/∆R is the same as the reciprocal of the weight-average molecular weight (Mw). The Mw established by fitting is (5.490 +/- 0.030) x 104 g/mol.
18.1 nm is the radius of gyration (Rg) determined by fitting. This radius of gyration is notably bigger than is usually expected from such a small molecular weight polymer. Usually, random coil polymers with a molecular weight under 75,000 g/mol are Rayleigh scatterers as their Rg is lower than 12 nm. The value of Rg established by light scattering is known as the average, an average weighted by the square of molecular weight. The high value of Rg can be explained by the fact that the PVP sample is polydisperse.
The next virial coefficient (A2) acquired by fitting is 4.33 x 10-4 cm3 mol/g2. As this value is positive, it suggests that water is a good thermodynamical solvent for PVP. For contrast, the second virial coefficient of molecular weight 55,000 g/mol PS in THF is 7 x 10 -4cm3mol/g2.
This data displays that the BI-MwA can be employed to establish the molecular weight of PVP.
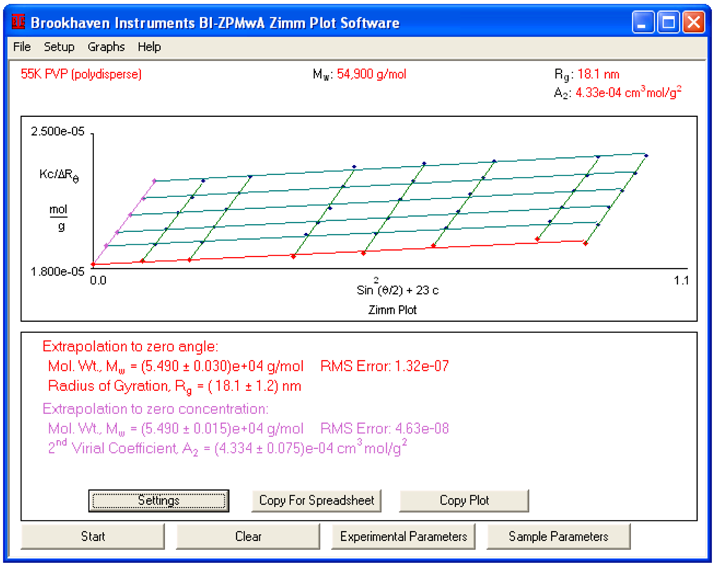
Image Credit: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Brookhaven Instrument Corporation.
For more information on this source, please visit Brookhaven Instrument Corporation.