Polylactic acid, (polylactide, PLA) polymers are employed in an extensive range of commercial, biomedical, academic and pharmaceutical applications due to their biodegradability and biocompatibility. Applications include sutures, stents, and a wide range of uses in food packaging and disposable tableware.
However, the molecular weight of the polymer can affect the properties of the end product. Therefore quick and reliable characterization is vital to better understand manufacturing performance, processing, and structure-property relationships.

Image Credit: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation
Molecular weight determination of PLA by solution-based techniques like Static Light Scattering (SLS) or GPC with refractive index detection is a challenge as a result of the low value for the refractive index increment, dn/dc. For example, the dn/dc of PLA in THF is 0.042 mL/g, this is 4.5 times less than a polystyrene solution with the same molecular weight and concentration in THF (dn/dc: 0.19 mL/g).
Image Credit: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation
An industrial PLA sample was dissolved in THF and data was collected with a BI-MwA in batch mode. Commercial polymers contain substantial amounts of impurities and dust, which are a huge problem in light scattering. The BI-MwA’s closed flow system prevents entry of airborne dust after filtration. Also, the BI-MwA’s software features automated dust rejection algorithms. Both features reduce the effects of dust on measurement results.
Light scattering data is typically analyzed with the Zimm equation:

Here, K is the Debye constant, a constant of the polymer/solvent system and proportional to the square of the refractive index increment, dn/dc1.
Polymer concentration, c, is determined when sample solutions are prepared, and ∆R is proportional to the excess scattered intensity and measured by the BI-MwA. The scattering vector, q is given by (4πn/λ)sin(θ/2). Here, n is the refractive index of the solvent, λ is the wavelength, and θ is the scattering angle
In order to determine molecular weight, the BI-MwA software generates a Zimm plot based on the Zimm equation. After extrapolation to zero angle and concentration, values for absolute molecular weight, Mw, radius of gyration, Rg and second virial coefficient, A2 are calculated and displayed.
For this sample:
Source: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation
| . |
. |
| Mw |
1.598 x 105 g/mol |
| Rg |
32.3 nm (indicating either a stiff polymer chain or a broad molecular weight distribution) |
| A2 |
1.18 x 10-3 cm3 mL/g2 (indicating that THF is a thermodynamically good solvent for PLA) |
This data shows that the BI-MwA can be used to determine the molecular weight of polylactides.
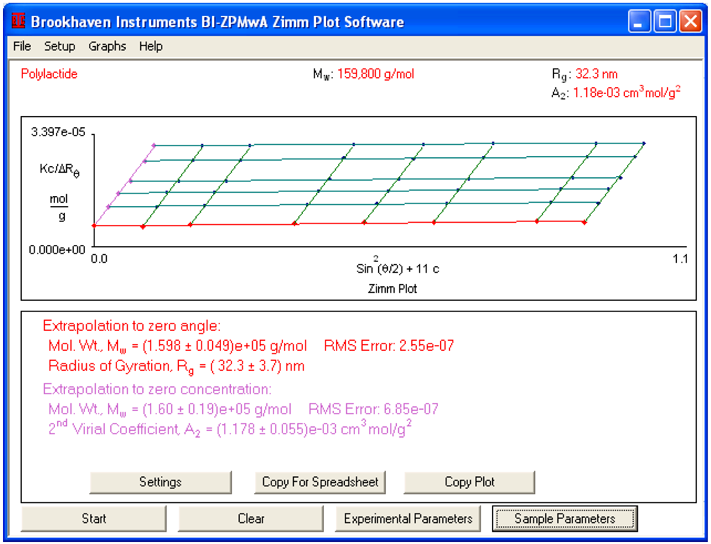
Image Credit: Brookhaven Instrument Corporation

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Brookhaven Instrument Corporation.
For more information on this source, please visit Brookhaven Instrument Corporation.