Polybutadiene (or rubber) is added during polymerisation of styrene to increase the flexibility of polystyrene polymers. It is important to closely monitor the amount of polybutadiene added, so that the flexibility of the polystyrene polymer may be regulated. NMR can provide an effective and rapid method for the regulation of polybutadiene content in Impact Polystyrene.
Advantages of Using NMR to Determine Pulybutadiene Content in Polystyrene
NMR has a number of advantages over other techniques:
- It can be calibrated to cover a range from 0 to 100%.
- The measurement time is short (typically 32 seconds), allowing for rapid sample throughput.
- The NMR technique is non-destructive, so polystyrene analysed is still usable.
- NMR is insensitive to air voids between polystyrene granules.
- NMR is very stable over the long-term, so calibrations will rarely require adjustment.
- NMR does not require the use of hazardous solvents.
- Both weighing and non-weighing methods are available for this application.
Method for Determining Polybutadiene Content of Polystyrene
12 samples of Impact Polystyrene were selected for the measurement of polybutadiene content. Each sample was weighed into a tared 26mm glass tube before measurement at room temperature in the MQC-23
Results and Calibration
Figure 1 shows the calibration generated from these samples. The graph illustrates the calibration of the NMR signal against a value of polybutadiene content obtained by a standard technique.
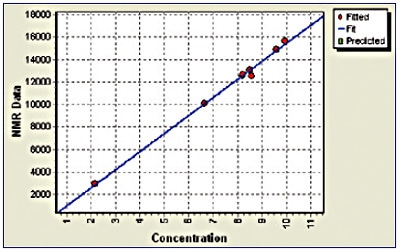
Figure 1. Calibration of NMR data and given polybutadiene content. Green squares indicate outliers. Correlation: r =1, SD = 0.15.
Table 1 shows the repeatability (or precision) of the NMR data is excellent.
Table 1. Repeatability of NMR measurement.
| Repeat Number |
Polybutadiene Content (%)
|
| 1 |
6.79
|
| 2 |
6.81
|
| 3 |
6.80
|
| 4 |
6.81
|
| 5 |
6.79
|
| 6 |
6.78
|
| 7 |
6.81
|
| 8 |
6.79
|
| 9 |
6.79
|
| 10 |
6.80
|
| Average |
6.80
|
| SD |
0.009
|
The MQC-23 Benchtop NMR Analyzer
MQC-23 fitted with a 26mm diameter (14ml sample) probe is a suitable instrument for this application. The Rubber in Impact Polystyrene package consists of:
- MQC-23 with a built in computer operating the latest version of Microsoft® Windows® (no separate PC is required).
- Multiquant software including RI Calibration, RI Analysis, and the EasyCal ‘Rubber in Polystyrene’ application.
- 26mm diameter glass tubes.
- Installation manual.
- ‘Rubber in Polystyrene’ method sheet.
- In addition to this package you may also require a precision balance.
The MQC-23 instrument offers advantages over others on the market:
- High signal sensitivity.
- Small benchtop footprint.
- Low maintenance.
- Recyclable sample tubes, lowering consumable costs.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Oxford Instruments Magnetic Resonance.
For more information on this source, please visit Oxford Instruments Magnetic Resonance.