In a recent study published in the journal Materials, researchers from China studied the improvement in properties of concrete due to the addition of graphene oxide (GO).
Study: Efficient Use of Graphene Oxide in Layered Cement Mortar. Image Credit: Daniel Ramirez-Gonzalez/Shutterstock.com
Concrete and Nanomaterials
Concrete is the most widely used construction material due to its high compressive strength and low cost. The main limitation of concrete is that it is a brittle material with low tensile strength and poor corrosion resistance. Furthermore, when Portland cement is manufactured, a significant amount of CO2 is released. Due to this, researchers worldwide are trying to improve concrete's durability and mechanical properties.
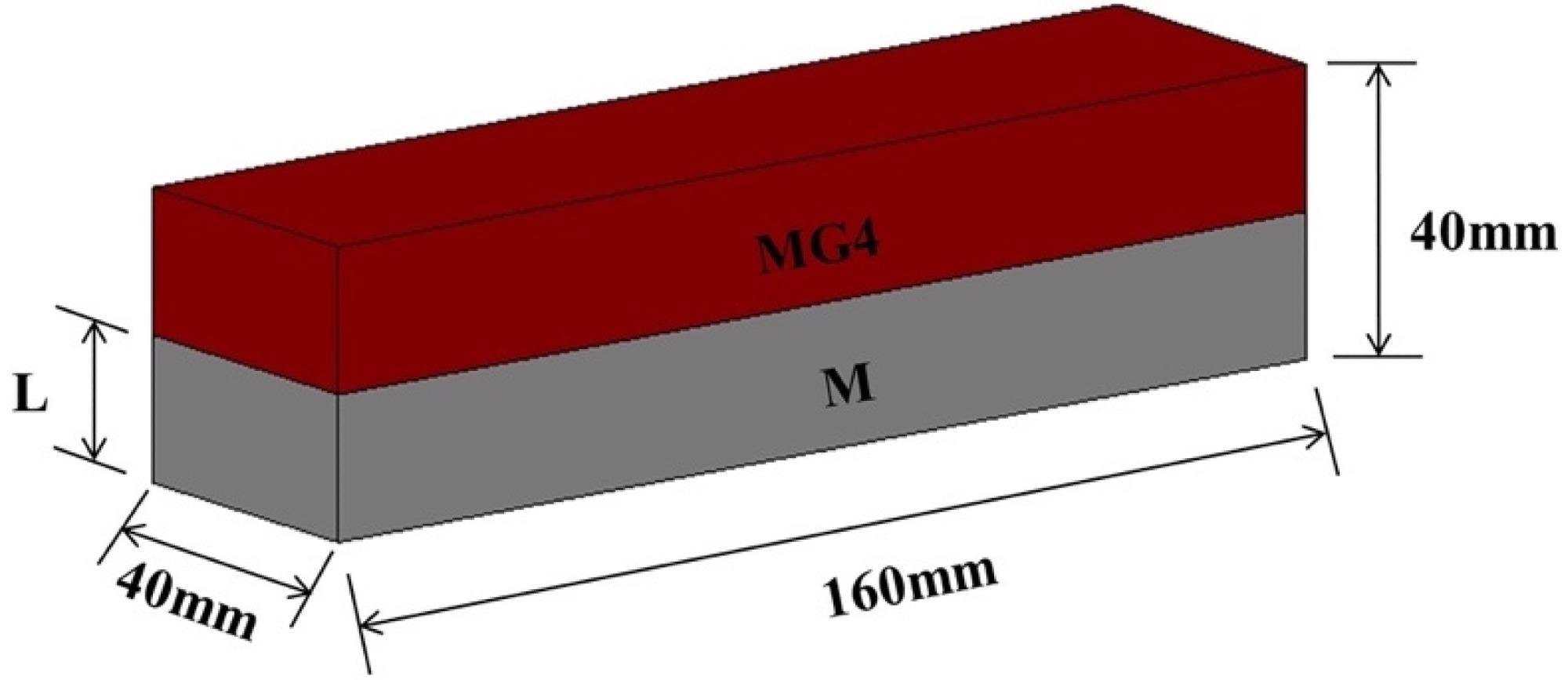
Geometry of layered cement mortar specimens. Image Credit: Liu, S et al., Materials
The advancement of nanomaterials has provided valuable opportunities to improve the properties of concrete in recent years. Several studies have demonstrated that nanomaterials like nano-silica, carbon nanotubes, and GO improve the strength, toughness, and durability of cement composites.
The present study analyzed the properties of layered cement mortar samples with a graded distribution of GO.
Methodology
The materials used by the researchers were ordinary Portland cement (OPC) grade, standard sand, and graphene. The cement and sand were used to prepare the concrete, and the graphene was used to prepare the GO suspension. The method used was wet-on-wet layering fabrication, during which a fresh cement mortar layer containing GO was cast on top of a previously casted cement mortar layer.
The researchers prepared two varieties of cement mortar samples: the first was plain cement mortar with no GO solution, and the second was GO-incorporated cement mortar. The water-to-cement and sand-to-cement mass ratios for both samples were 2.0 and 0.4, respectively. Additionally, to ensure that the samples had comparable workability, the amount of superplasticizer was adjusted, and a mini-slump test was used to determine workability.
The mortar mixture was cast into molds and mixed on a vibration table to ensure high compaction during sample development. The molds were enclosed with polyethylene sheets, and further, the samples were molded and treated in a saturated limewater bath before testing to prevent water evaporation. Successive layers of fresh cement mortar and cement mortar with GO were cast to prepare the layered cement mortar beams with the graded distribution of GO.
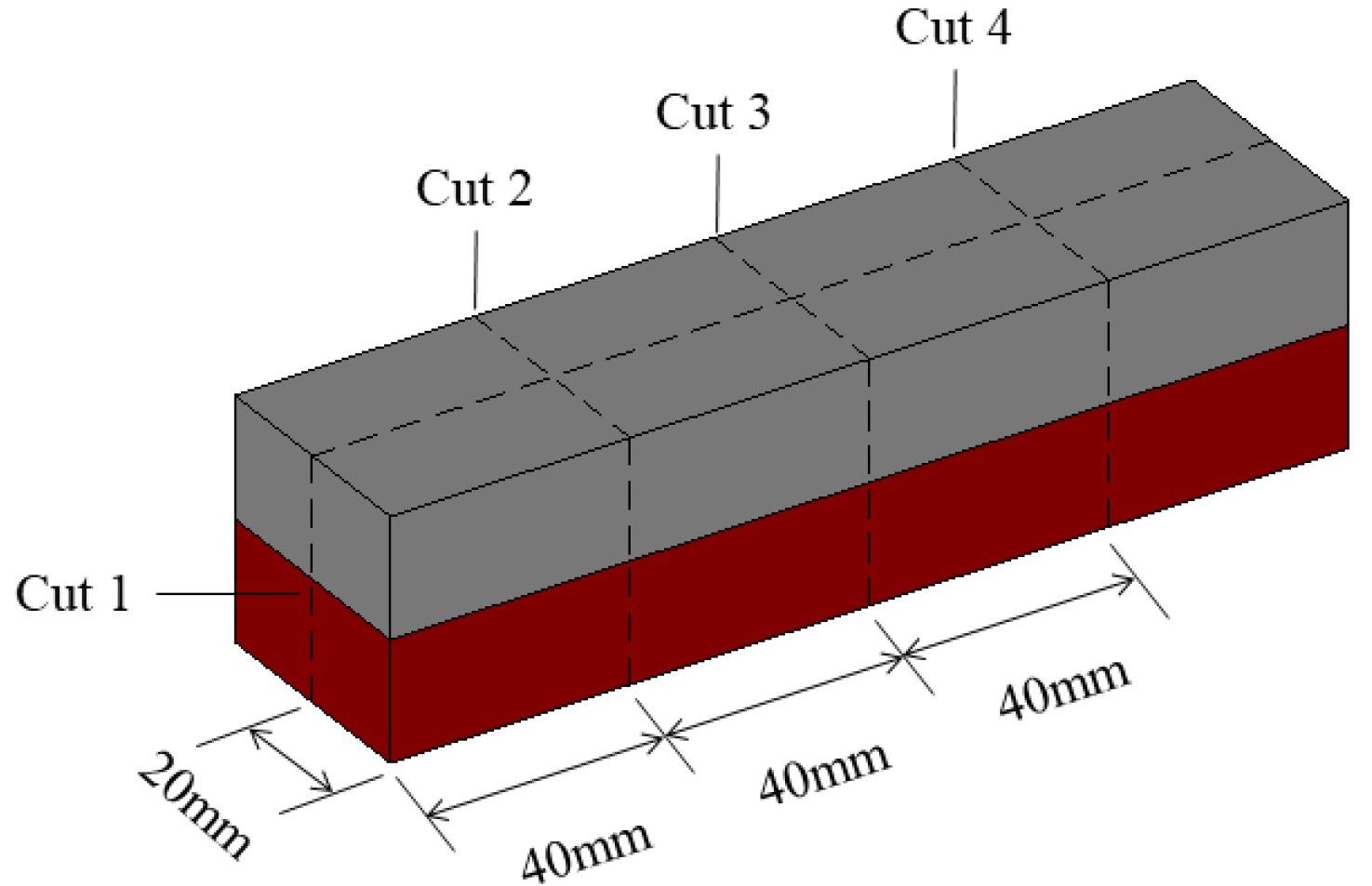
Four cut locations of each sample. Image Credit: Liu, S et al., Materials
Results
The plain cement mortar sample's scanning electron microscope (SEM) images showed a loose and porous microstructure. The SEM images of the GO-added cement mortar sample revealed a denser structure. The improvement in the GO-incorporated mortar cement mechanical properties resulted from changes in the microstructure of cement.
The flexural strength results revealed that the strength increased to a maximum and then decreased as the delay time increased. Additionally, the strength was not dependent on the thickness of the cement layer. The highest flexural strength was found with a GO layer thickness of 12 mm and a delay time of 50 minutes. The maximum flexural strength was dependent on the delay time for the samples with different GO layer thicknesses.
The study of images of the layered cement mortar beams after flexural failure revealed a significant difference in crack development between the GO layered and plain cement mortar beams. In the plain cement mortar, the beam crack was completely vertical and had a relatively flat fracture surface.
On the layered cement mortar beam containing GO, inclined and tortuous cracks were observed. Additionally, compared to the control sample, the properties of the layered cement mortar beams did not change when the GO was added only in the tensile region of the samples. However, the interface developed between the layers of the samples considerably influenced the mechanical properties. Furthermore, the interface adhesion was also affected by the delay time and amount of GO in the samples.
The rapid chloride migration (RCM) tests revealed that a small quantity of GO could significantly reduce chloride ingress, and when the amount of the GO was enhanced, the RCM effect also increased. The reason for increment was that GO nanosheets' presence increased the cement matrix's tortuosity, which immobilized water and chloride ion migration through chemical bonding.
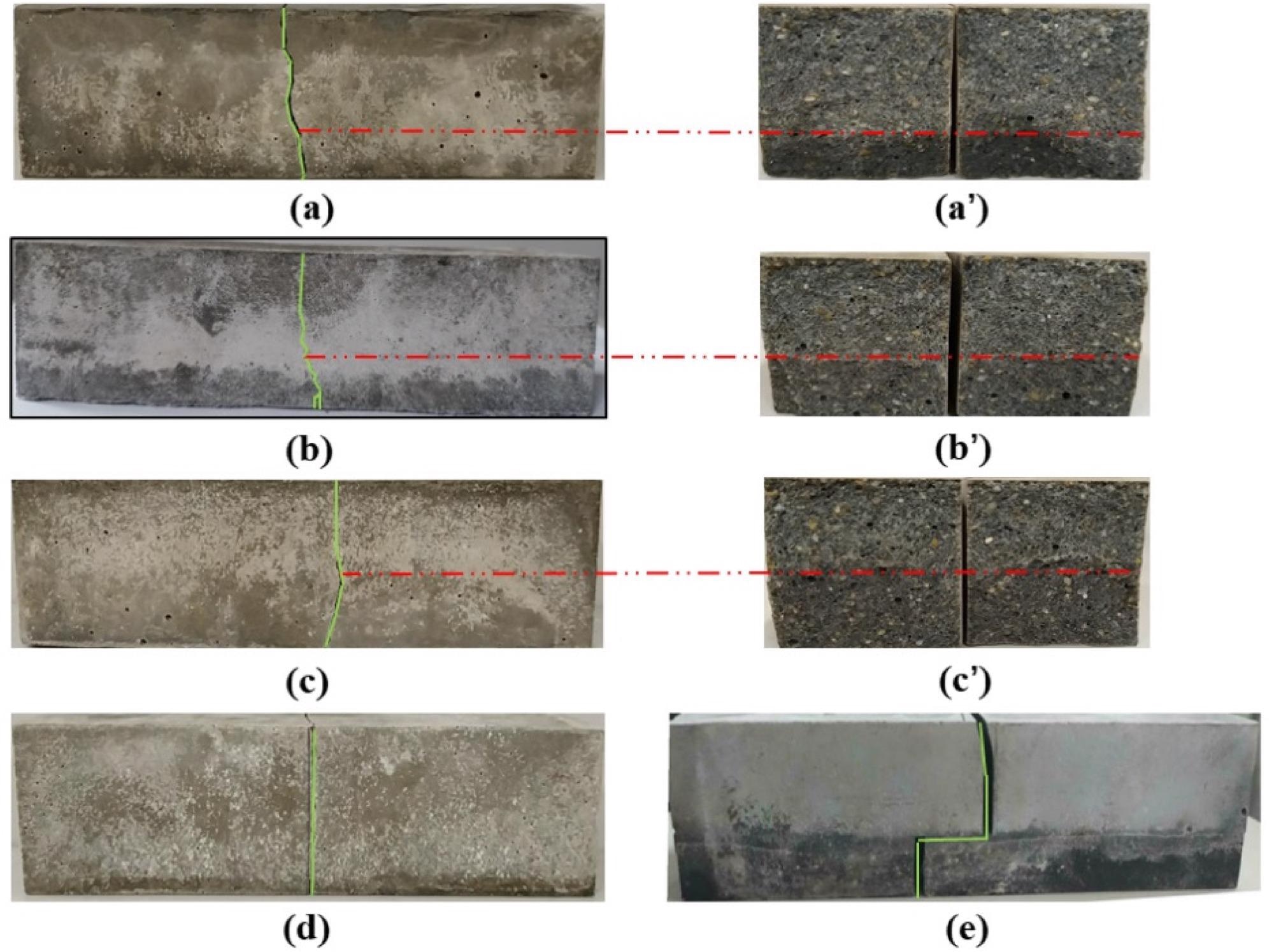
Crack development of samples: (a) L8T50, (b) L12T50, (c) L16T50, (d) M, and (e) L12T300. Fractured surfaces of samples: (a’) L8T50, (b’) L12T50, (c’) L16T50. Image Credit: Liu, S et al., Materials
Conclusions
The researchers developed functionally graded cement mortar beams using successive layers of mortar cement and GO-incorporated mortar cement. The effects of the thickness of each GO-incorporated cement mortar layer and the delay time on the mechanical and durability properties were investigated.
The study demonstrated that the nanomaterial GO could be used in parts of cementitious composites to improve the mechanical properties. This method provides a novel approach to use nanomaterials effectively in cement-based materials. Future research should study the ways to improve interfacial adhesion between GO-incorporated cement mortar layers and cement mortar layers without GO.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
Liu, S.; Lu, F.; Chen, Y.; Dong, B.; Du, H.; Li, X. Efficient Use of Graphene Oxide in Layered Cement Mortar. Materials 2022, 15, 2181. https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/6/2181