Reviewed by Mila PereraSep 23 2022
In the fields of catalysis, ion exchange, and adsorption/separations, zeolites are significant inorganic crystalline microporous materials with a wide range of applications.
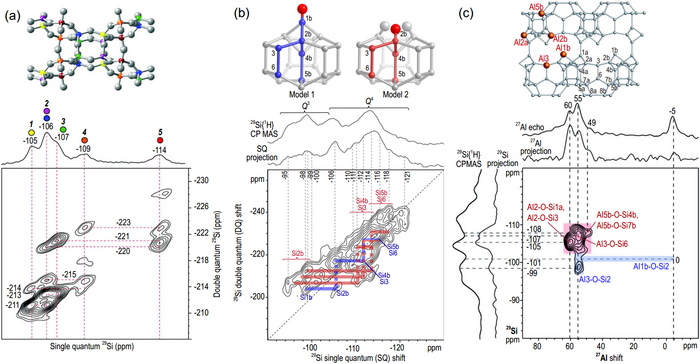
(a) 2D refocused INADEQUATE (J-mediated) 29Si{29Si} DQ NMR spectrum of as-synthesized zeolite ITW. (b) DNP-enhanced 2D 29Si{29Si} J-mediated correlation spectrum of calcined Si-SSZ-70. (c) Schematic diagram of the framework structure of Al-SSZ-70 (orange color indicates the T sites that are occupied by Al heteroatoms), and 2D 27Al{29Si} J-HMQC NMR spectrum of calcined Al-SSZ-70. Image Credit: Science China Press
Zeolites are one of the most significant heterogeneous catalysts utilized in the petrochemical and fine chemical industries due to their distinctive pore structure, excellent heat stability, and tunable acid-base properties.
Developing efficient zeolites with improved properties depends on understanding the structure-activity relationship, which requires a fundamental characterization of the zeolites.
Solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy is a well-established method for researching zeolites and associated catalytic reactions due to its utility in offering atomic-level insights into molecule structure and dynamic behavior.
Scientists from the State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences in Wuhan, China, summarize the most recent developments in ssNMR of zeolite catalysts in a new review published in the Beijing-based National Science Review.
The review focuses on the new applications of ssNMR to investigate zeolite framework structure, catalytically active sites, and intermolecular interactions. The authors also discuss the ssNMR technique’s present limitations and potential future uses for zeolite catalysts.
According to the authors, when combined with cutting-edge equipment and experimental methods, ssNMR has proven a potent analytical tool for zeolites’ characterization. Using multiple 1D and 2D ssNMR techniques, framework structure and acid sites can be directly detected.
Scientists studying zeolites have increased their catalytic performance in various crucial reactions, including the oligomerization of alkenes, the cracking of hydrocarbons, and the conversion of methanol.
In the meantime, ssNMR can investigate the internuclear spatial proximities connected to host-guest and guest-guest interactions in zeolites using 1D and 2D correlation spectroscopy.
Scientists can better understand zeolite production, adsorption/desorption, and catalytic reactions by characterizing different interactions. The use of ssNMR for observing and identifying crucial active intermediates in zeolite-catalyzed reactions has emerged as a major strategy for understanding reaction mechanisms.
The knowledge of the reaction mechanism and the intermediates has been used to synthesize new zeolites able to control the reaction pathway in a complex reaction.
Journal Reference
Wang, W., et al. (2022) Recent advances in solid-state NMR of zeolite catalysts. National Science Review. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwac155.