
In order to properly maintain and ensure the proper function of many types of machinery, it is crucial to analyze additives or wear metals in lubricating oils and the contaminants in fuel. There are increasingly stringent testing requirements for marine, military, aircraft, mining, and trucking equipment, as well as heavy transportation.
There is a crucial need in many fields for machine operators to analyze lubricating oils and fuel quickly and accurately. These requirements can be met by the Vanta handheld XRF analyzer, developed by Evident. Its oil analysis method enables fast analyses with minimal sample preparation.
Operators are given on-site analysis in real-time, and can measure key wear metals such as chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), iron (Fe), and copper (cu), courtesy of the Vanta XRF analyzer. The analyzer can also measure numerous regulated or secondary metals, such as cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), molybdenum (Mo), and manganese (Mn).
Key fuel additives’ concentrations can also be measured by the Vanta analyzer, including zinc (Zn), calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), and phosphorus (P), in accordance with ASTM D6481. Courtesy of the Vanta analyzer’s routine testing, operators can identify small issues before they grow into expensive failures.
Wear Metal and Secondary Metal Analysis
One of the most effective ways of detecting potential machine failures prior to them becoming too expensive and serious is wear metals’ analysis. Potential failures can help to be predicted by metallic elements in lubricating and engine oil. These elements can also help to identify the failing component. The quick detection of elevated metal concentrations early on is crucial to the effectiveness of such testing.
Operators also generally monitor a number of secondary metals, including alloying elements such as Mn and Mo as well as heavy metals such as Cd and Hg. Such elements can be used as indicators for both regulatory compliance and engine performance. Operators are able to analyze in search of as many as thirty-one separate elements in just seconds, which identifies potential failures inside engine systems.
Oil Additive Analysis
The best quality lubricants depend upon specially formulated blends of organometallic additives in order to protect precision equipment which operates under heavy loads or extreme temperatures. These additives protect metal surfaces, increase the range in which a lubricant can be used, and extend lubricant life.
Such additive elements as zinc and calcium contribute to crucial lubrication characteristics, while elements such as phosphorus and sulfur are vital for extreme pressure lubricants. The expense of routinely dismantling components for visual inspection is reduced by a robust maintenance program, which routinely measures the metals and additives in lubricating oils and helps to identify worn components prior to failure.
Guidance on how to monitor these additive elements for potential depletion is provided by ASTM 6481. For meeting the criteria set by this standard, the Vanta handheld XRF analyzer’s repeatability and sensitivity capabilities are effective.
VCA Model Oil Repeatability Comparison
| Element |
Concentration (PPM) |
D6481 Required Repeatability (PPM) |
VCA Repeatability (PPM) (Lower is Better) |
| P |
100 |
60.0 |
36.0 |
| S |
150 |
9.7 |
6.0 |
| Ca |
4000 |
56.5 |
46.4 |
| Zn |
1000 |
18.4 |
8.0 |
Vanta XRF Analyzer Performance
As a means of demonstrating the performance capabilities of the Vanta analyzer, numerous certified oil samples were tested with several levels of additive elements, secondary metals, and wear metals using a VCA model (Vanta C-series silver anode analyzer). Samples were collected in the same manner as plastic bottles with Prolene® windows for XRF measurement. The averages of five repeated tests, when compared against the value of the lab assay, are shown in the results.

Wear Metals
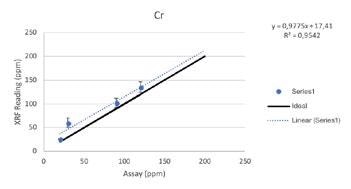
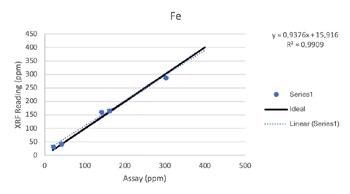
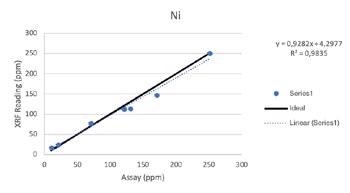
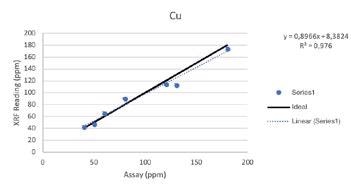
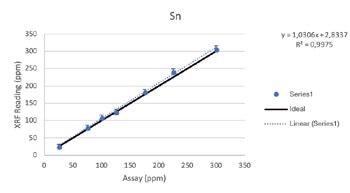
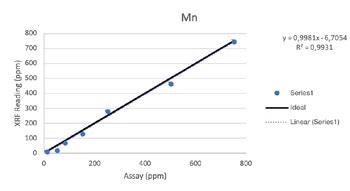
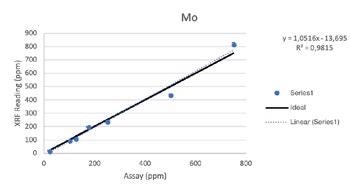
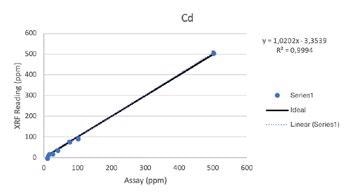
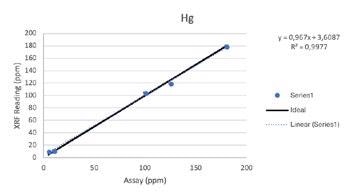
Secondary Metals
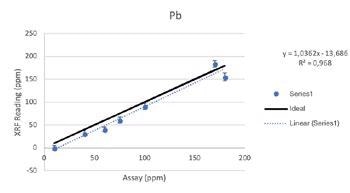
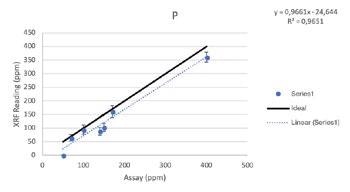
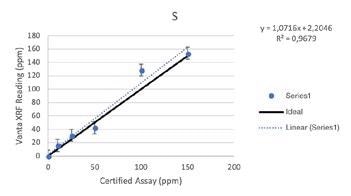
Additive Elements
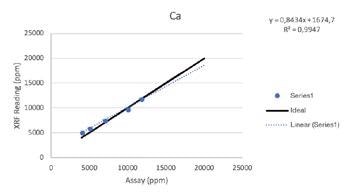
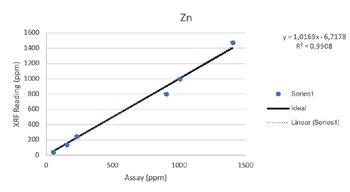
Due to the heterogeneous nature of metals in oil, oil analysis is prone to high variability. The sensitivity and accuracy of a variety of additive elements and transition metals can also be affected by inter-elemental effects.
Regardless of such limitations, all of the elements above were able to be tested by the Vanta analyzer with a high consistency and repeatability (R2>0.95 for all elements). For secondary metals and wear metals, trend lines were within 5% of the lab assay. For the additives, they were within 16% of the assay values.
Conclusion
Wear metal and secondary metal content at low-ppm levels can be measured accurately and effectively by the Evident Vanta handheld XRF analyzer, enabling the accurate monitoring of engine oil.
In accordance with ASTM D6481, the Vanta analyzer is also able to test for fuel additive elements. An effective combination of being easy to use, quality performance, and good sensitivity capabilities, helps the Vanta XRF to give engine and machine operators the confidence they need.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Evident (XRF / XRD).
For more information on this source, please visit Evident (XRF / XRD).