Salts of lithium, such as lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate, are used in various applications, for example, the production of cathode and electrolyte materials in lithium ion batteries.
In addition, lithium hydroxide is used to produce lithium stearate, a vital lubricant for airplanes and cars. Thanks to its carbon dioxide-binding ability, it is also used as an air purifier.
Lithium carbonate is mainly used for producing aluminum, but it also finds use in the glass and ceramic industry. It is used to lower the melting point of aluminum, glass, and ceramics. This reduces the electricity costs associated with the production of these materials. It is also used in the treatment of mental illnesses such as bipolar disorder or depression.
For all the applications mentioned above, it is crucial to know the quality of the pure lithium salts used in the different production processes. This article describes a simple method for the assay of lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide on an automated OMNIS system.
Sample and Sample Preparation
The sample preparation step is not required because lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide can be analyzed directly. For the lithium hydroxide assay, care should be taken to ensure that the water does not contain any carbon dioxide. Otherwise, it would hinder the titration.
Experiment
Both assays are performed on an automated system that is equipped with an OMNIS Sample Robot S and an OMNIS Advanced Titrator provided with dEcotrode plus (see Figure 1).

Figure 1. Sample Robot and OMNIS Titrator Advanced equipped with dEcotrode plus for the assay of lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate. Image Credit: Metrohm AG
Once the sample is weighed and transferred into the beakers, the system automatically performs the dilution and titration of the sample. Hydrochloric acid is used for titration of the sample until after the equivalent point.
Results
Reproducible results with relative standard deviations less than 0.4% (n = 5) were obtained for both assays (see Table 1). Moreover, carbonate impurities contained in the lithium hydroxide sample can also be detected.
Table 1. Results of the assay of lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate.
| n = 5 |
Purity of LiOH in % |
Purity of Li2CO3 in % |
| Mean |
99.20 |
100.78 |
| SD(abs) |
0.24 |
0.34 |
| SD(rel) |
0.24 |
0.34 |
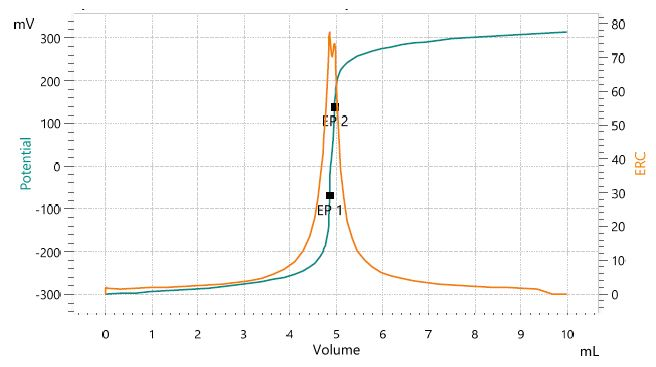
Figure 2. Titration curve of the assay of lithium hydroxide. The second equivalence point corresponds to lithium carbonate impurities. Image Credit: Metrohm AG
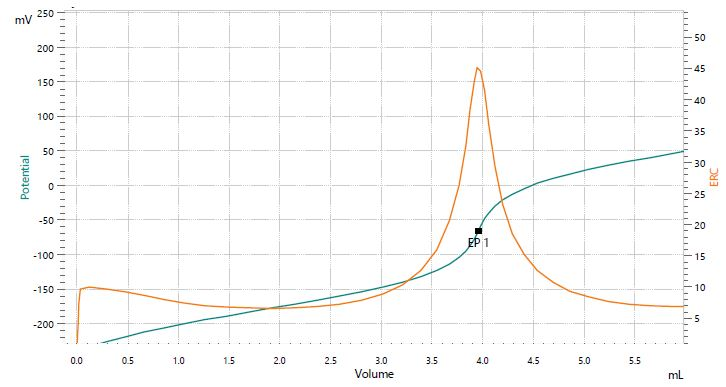
Figure 3. Titration curve of the assay of lithium carbonate. Image Credit: Metrohm AG
Conclusion
Titration is a reliable and accurate method for the assay of lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide.
An automated OMNIS system enables users to analyze up to four samples at the same time. It is possible to customize the OMNIS system according to user requirements. It can also be expanded for other titration applications needed for quality control.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Metrohm AG.
For more information on this source, please visit Metrohm AG.