Honey has been recognized for its medicinal and therapeutic properties for some time. The sticky golden-yellow liquid is ubiquitous across time and nations. The chemical has been used to treat skin disease, cancer, heart disease, neurological degeneration, and wound healing, and it is anti-inflammatory and antibacterial.1
These characteristics have been attributed to the minor ingredients contained within, which include phenolics, flavonoids, flavones, and flavonols.2 Honey production, which requires bees to generate the sticky sweet material, results in a high market price.
As a result, it is a popular target for adulteration with refined sugars to extend the supply or increase earnings.3 The contamination reduces the product's shelf stability and decreases its overall health advantages.
Similarly, the intricacy of natural honey does not lend itself well to a reproducible scientific signature, because each batch of honey produced is reliant on the specific flowers consumed by the bees. Because no two blooms are the same, each one produces a unique chemical profile of honey.
The ratio of carbohydrates in honey remains pretty stable. The fructose, glucose, and sucrose have a ratio of approximately 1.2:1:0.1.4. Large deviations from this ratio indicate that the honey has been debased.
The main carbohydrate profile was investigated using a Hamilton cation exchange HPLC column (HC-75 Pb2+ form) with only DI water as a mobile phase. Local honey obtained in northern Nevada exhibited low variation in the carbohydrate ratio, and the associated analysis revealed a link to the expected carbohydrate ratio.
Source: Hamilton Company
| Column Information |
| Packing Material |
HC-75 (Pb2+ Form), 9 µm |
| P/N |
79438 |
| Chromatographic Conditions |
| Gradient |
Isocratic |
| Temperature |
80 °C |
| Injection Volume |
25 µL |
| Detection |
Refractive Index |
| Dimensions |
305 x 7.8 mm |
| Eluent A |
Water |
| Flow Rate |
0.8 mL/min |
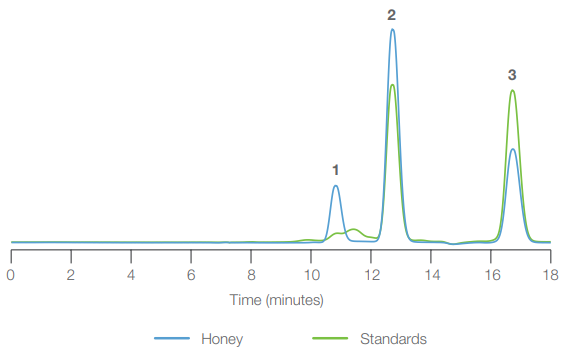
Compounds: 1: Sucrose 2: Fructose 3: Glucose. Image Credit: Hamilton Company
References
- S. Hussein, K. Yusoff, S. Makpol, Y. Yosof, Molecules 16 (9) 2011, 6378 – 6395.
- Karabagias, I.K., Dimitriou, E., Kontakos, S. et al. Eur Food Res Technol 242, 2016, 1201–1210 .
- S. Bogdanov, P. Martin, Mitt. Lebensm Hyg. 93, 2002, 232-254.
- H.I. Alijohar, H.M. Maher, J. Albaqami, M. Al-Mehaizie, R. Orfali, R. Orfali, S. Alrubia. Saudi Pharm. J. 26, 2018, 932 – 942.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Hamilton Company.
For more information on this source, please visit Hamilton Company.