Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) can be defined as miniaturised mechanical and electromechanical elements (i.e., devices and structures) that are made using the techniques of microfabrication. MEMS are commonly used as actuators, sensors, and radio frequency and microfluidic components all of these with a wide range of applications across a variety of fields including health care, automotive, and military industries.
These MEMS devices can match or even exceed the performance of their conventional counterparts, however, with smaller volume, lower weight, and significant lower production costs. There are however, considerable challenges in the fabricating and packaging such devices. In particular, diverse issues related to yield and reliability need to be overcome.
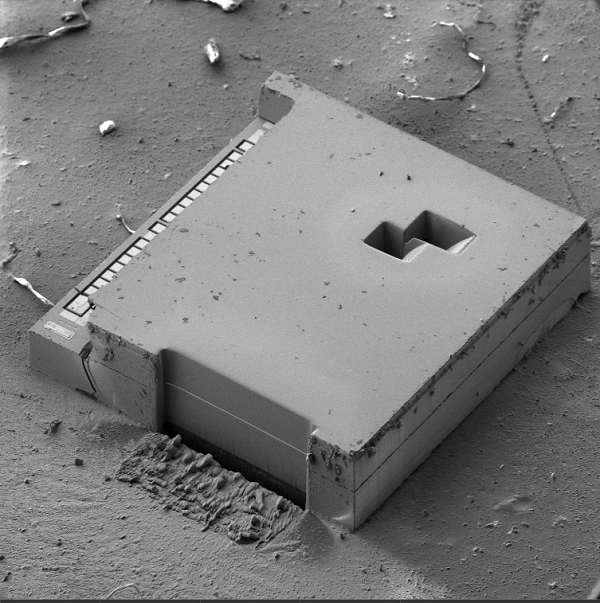
Fig 1. MEMS with multiple cross-sections through the bonding layer of W2W cavity die.
Inertial structures for motion sensors are generally composed by Wafer-to-Wafer (W2W) cavity die. The lid is bonded to the sensor with a metallic material (Fig. 1). Routine failure analysis consists in examining manufacturing defects in the bonding layer that lead to malfunction. For this purpose, large-area cross-sections at specific locations on the MEMS device need to be prepared. These cross-sections are conventionally prepared by mechanical polishing, a technique which indeed enables large-area cross-sectioning, but on the other hand, induces severe artefacts such delamination, tearing, mechanical stress or even the total destruction of a part of the die. Besides, it is difficult to keep a good control on end pointing.

 Want to know more? Click here to read the full article.
Want to know more? Click here to read the full article.
TESCAN Group
Founded in 1991 by a group of managers and engineers from Tesla with its electron microscopy history starting in the 1950’s, today TESCAN is a globally renowned supplier of Focused Ion Beam workstations, Scanning Electron Microscopes and Optical Microscopes. TESCAN’s innovative solutions and collaborative nature with its customers have won it a leading position in the world of nano- and microtechnology. The company is proud to participate in premier research projects with prominent institutions across a range of scientific fields. TESCAN provides its clients with leading-class products in terms of value, quality and reliability. TESCAN Group is the North American arm of TESCAN Group, a multinational company established by the merger of Czech company TESCAN, a leading global supplier of SEMs and Focused Ion Beam workstations, and the French company ORSAY PHYSICS, a world leader in customized Focused Ion Beam and Electron Beam technology.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by TESCAN Group.
For more information on this source, please visit TESCAN Group.