Deep learning innovations are leading to novel fields of application for industrial image processing, including applications that were previously either not viable at all or only viable with significant effort.
New approaches to image processing are significantly different from many existing methods, presenting challenges and often steep learning curves for users.
To help ease this transition, IDS has developed an all-in-one embedded vision solution that allows any user to integrate AI-based image processing into their applications, using a camera that functions as an embedded inference system.
IDS’ inference systems can be set up rapidly, easily and without the need for complex programming knowledge - deep learning is now far more accessible and user-friendly than ever before.
Computer vision and image processing solutions are essential in various sectors and industries, with these systems frequently being required to adapt to a continually expanding range of products, variants and organic objects; for example, fruit, vegetables or plants.

Artificial intelligence can easily handle varying object conditions. Image Credit: IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
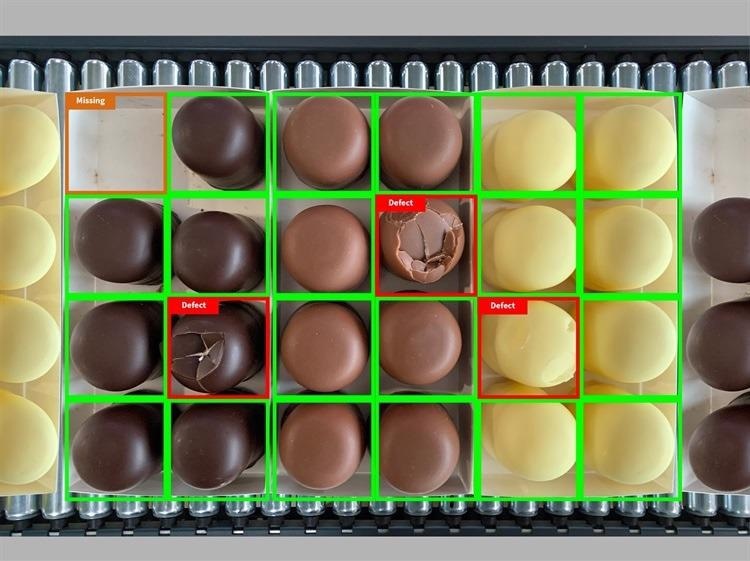
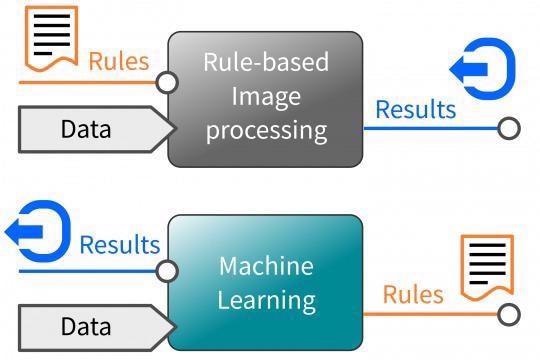
Rule-based image processing approaches are faced with notable limitations when utilized in applications where the image data analyzed often varies or where this exhibits differences that are difficult or impossible to describe using algorithms.
These inflexible sets of rules mean that robust automation is not a viable option for these applications.
Many tasks that cannot be managed via rule-based approaches would be easy for a human being to solve - a child could recognize a car, even if they had not previously seen that specific model. The child would have seen other car types and models before, enabling recognition.
Machine learning has the potential to facilitate flexible and independent decisions, capabilities that can now be employed in image processing systems.
Through the use of neural networks and deep learning algorithms, it is now possible for a computer to observe objects, recognize objects and reach appropriate conclusions from what it has learned during this process.
This works in a similar fashion to a human being’s learning process, with intelligent automation learning using empirical values to make informed decisions.
Differences to Conventional Image Processing
The key difference between deep learning and rule-based image processing is the way in which - and by whom - image characteristics are recognized and how this learned knowledge is characterized.
The traditional symbolic approach sees an image processing expert defining decisive image features prior to describing these according to certain rules.
As the software is only able to recognize features that the rules cover, this means that many lines of source code are necessary to provide enough detail to complete a given task.
Execution of the task takes place within defined limits with no room for interpretation – every intellectual consideration remains the sole responsibility of the image processing specialist.
Neural networks differ considerably from this rule-based approach, primarily due to their capacity to independently determine which image characteristics must be considered to draw the most appropriate conclusion.
This can be understood as a non-symbolic approach. The knowledge is implicit, and this does not allow insight into any of the solutions learned. The stored characteristics, weighting, and conclusions drawn are impacted solely by the content and quantity of the training images.
Deep learning algorithms can recognize and analyze the complete image content. Recognized characteristics are related to terms that are learned depending on how often these occur.
It is possible to understand the statistical frequency of these characteristics as ‘experience’ during training.
Machine Learning: teach through examples. Image Credit: IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
Cassie Kozyrkov - an artificial intelligence specialist at Google - described machine learning as a programming tool at the 2019 WebSummit in Lisbon, relating this to a tool that uses examples to teach a machine rather than explicit instructions.
This definition should prompt a reconsideration of the development of machine vision applications based on AI. Result quality – for example, the reliability and speed of object detection – is highly dependent on a neural network’s potential to detect features and reach conclusions.
The experience and expertise of the person setting up the network are vitally important because they must ensure that appropriate data sets are available for training. These data sets must include as many different example images as possible, ensuring that these feature the terms to be learned.
Historically, the traditional approach saw this responsibility fall to an image processing specialist. In machine learning, however, this becomes the responsibility of a data specialist.
The Challenges of Developing Novel AI Applications
Examining the individual steps involved in the development of an AI application uncovers tasks and concepts which are entirely different from the development stages typically associated with the traditional approach.
New tools and development frameworks are required to effectively handle and prepare image data and to train neural networks. Each of these tools and frameworks must be installed and executed on an appropriate PC infrastructure.
Both guidance and open-source software are typically freely available from cloud providers or on platforms such as Github, but these tend to only include basic tools which necessitate a high degree of experience to operate.
The creation, execution and evaluation of training results on a suitable hardware platform using these open-source tools rely on operator knowledge and experience of hardware, software and the interfaces between these application layers.
Lower entry barrier with easy-to-use tools. Image Credit: IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
An All-in-One Solution to Machine Learning
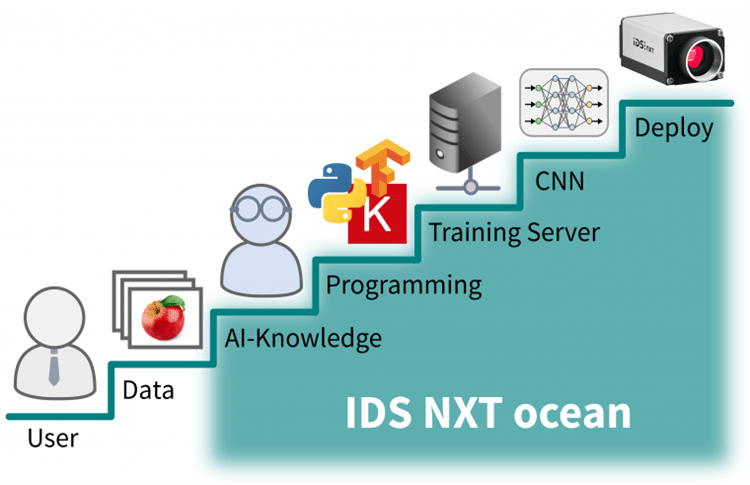
IDS aims to support users throughout this process, from their first steps using this new technology to more advanced use, achieving this via a deep learning experience and high-end camera technology provided in an all-in-one inference camera solution.
AI-based image processing is immediately available to all users thanks to IDS’ NXT Ocean. This system significantly lowers the barrier to entry for AI imaging applications, and its series of easy-to-use tools is able to generate inference tasks designed for execution on a camera in minutes, even with minimal prior knowledge.
The system is comprised of three core components:
- An intelligent camera platform
- Accessible neural network training software
- An AI accelerator able to execute neural networks on the hardware
IDS has developed each of these individual components to seamlessly work together, ensuring a powerful, user-friendly system.
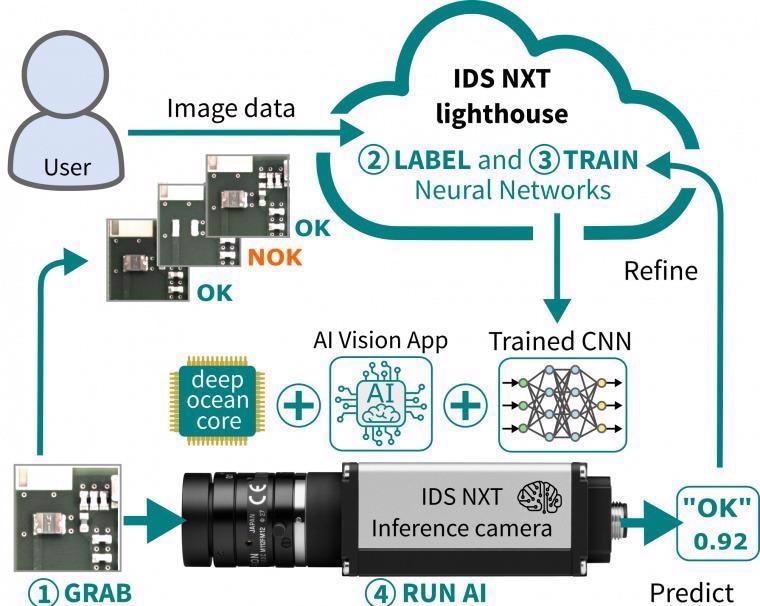
The IDS NXT lighthouse cloud-based training package has been designed to guide users through the data preparation and neural network training processes without the need to engage with advanced tools or install development environments.
As it is a web application, IDS NXT lighthouse is available on demand. The application features an intuitive workflow, storage space and appropriate training performance - the user only has to log in, upload and label training images to begin training the desired network.
Other benefits of this system include exceptional data protection and security, facilitated via a reliable data center and robust network architecture of German servers provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Users are able to define an applications’ speed and accuracy requirements using a series of user-friendly dialogs and configuration settings. IDS NXT lighthouse will then select the network and set up the required training parameters independently.
Once training has been completed, the results provide an indication of the quality of the trained intelligence, allowing users to then modify and repeat the training process until the desired level of accuracy is achieved.
The IDS lighthouse system continues to be improved and upgraded, while its web-based delivery ensures that the latest version is constantly available - users are not required to manage updates or maintain the system.
The training software makes use of supervised learning to train neural networks, employing deep learning algorithms via predefined input/output pairs. The user provides the function value for input by assigning the correct class to an example image.
The network makes these associations independently, making predictions around image data and presenting these as percentages. Higher values represent a more reliable, accurate prediction.
Once neural networks have been fully trained, these are uploaded and executed directly on the IDS NXT cameras. No additional programming is necessary, and the user has instant access to a completely operational embedded vision system with the capacity to see, recognize and generate results from any image data captured.
The cameras’ digital interfaces (for example, REST and OPC UA) also allow machines to be directly controlled.
Seamless interaction of soft- and hardware. Image Credit: IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
Embedded Vision Hybrid System
An AI core has been developed by IDS that is compatible with the FPGA of the intelligent IDS NXT camera platform.
The Deep Ocean Core can be used to execute pre-trained neural networks via hardware acceleration, effectively transforming industrial cameras into high-performance inference cameras. These capabilities afford users highly beneficial artificial intelligence capabilities ideal for an array of industrial environments.
Image analysis in these systems is performed in a decentralized fashion, mitigating any bandwidth bottlenecks which may occur during transmission.
Cameras based on the IDS NXT platform are able to confidently keep pace with current desktop CPUs, offering equivalent accuracy and speed with considerably reduced energy and space requirements.
The FPGA can also be reprogrammed relatively simply. This provides further benefits in terms of future security, minimal recurring costs and reduced time to market.
Extendable funtionality using apps and CNNs. Image Credit: IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
Leveraging the robust combination of IDS' software and hardware allows users to choose the target inference time before training. IDS NXT lighthouse will then select optimal training settings based on the camera’s AI core performance.
This approach allows the user to anticipate and address issues occurring during inference execution, eliminating the need for time-consuming readjustment or retraining.
Upon integration, the IDS NXT system will continue to exhibit compatible, consistent behavior – an essential requirement for many industrially-certified applications.
Extendable Functionality via Apps and CNNs
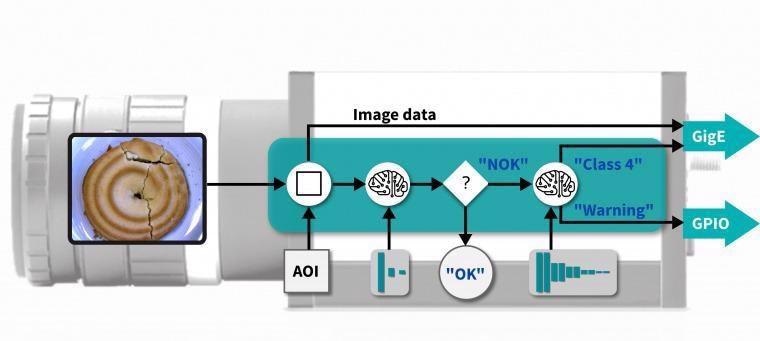
The robust and powerful hardware underpinning the embedded vision platform allows it to offer far more than a standard inference camera for executing neural networks - the innovative CPU-FPGA combination provides a feature set that can be easily expanded to meet a wide range of applications requirements.
It is possible to easily set up and change recurring vision tasks, enabling the execution of a fully flexible image processing sequence where required. Captured images may also be pre-processed; for example, by utilizing a basic classification process to differentiate between good and bad components.
When errors are detected, this can prompt the loading of a complex and comprehensive neural network (taking just milliseconds) to further determine the class of error in more detail prior to storing the results in a database.
An app development kit is also available, allowing the straightforward implementation of highly customized solutions and individualized vision apps that can be installed and run on IDS NXT cameras.
IDS NXT cameras have been specifically designed to operate as hybrid systems. These cameras can facilitate the pre-processing of image data, as well as image processing and feature extraction via neural networks, a combination that allows a single device to efficiently run a range of image processing applications.
Summary
IDS NXT ocean’s combination of hardware and software is ideally matched, enabling a wide range of industries to leverage the power of meaningful, user-friendly deep learning applications.
It is now easier than ever to set up automated, intelligent detection tasks in a number of fields, opening up a number of previously impossible applications.
Users are able to create and execute AI-based image processing solutions without programming knowledge, and the cloud-based IDS NXT lighthouse training software provides storage space and training performance that can be scaled according to specific user requirements.
As the software is cloud-based, the latest version is always available for every user - no updates or maintenance periods are necessary.
IDS also provides a cost-effective, convenient inference starter package that includes every component needed to facilitate the initial steps into AI-based image processing: a camera with a power supply and lens and a training license for IDS NXT lighthouse.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH.
For more information on this source, please visit IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH.