Apr 28 2010
Using a pair of exotic techniques including a molecular-scale version of ice fishing, a team of researchers working at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed methods to measure accurately the length of "nanopores," the miniscule channels found in cell membranes. The "molecular rulers" they describe in a recent paper* could serve as a way to calibrate tailor-made nanopores-whose diameters on average are nearly 10,000 times smaller than that of a human hair-for a variety of applications such as rapid DNA analysis.
Studies at NIST and other research institutions have shown that a single nanometer-scale pore in a thin membrane can be used as a "miniature analysis laboratory" to detect and characterize individual biological molecules such as DNA or toxins as they pass through or block the passage. Such a system could potentially fit on a single microchip device, for a wide variety of applications. However, making the mini-lab practical requires an accurate definition of the dimensions and structural features of the nanopore.
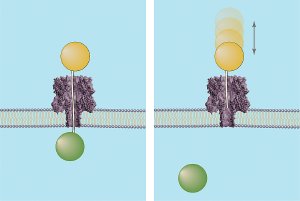
In new experiments, researchers from NIST and the University of Maryland first built a membrane-a bilayer sheet of lipid molecules-similar to that found in animal cells. They "drilled" a pore in it with a protein** designed specifically to penetrate cell membranes. When voltage is applied across the membrane wall, charged molecules such as single-stranded DNA are forced into the nanopore. As the molecule passes into the channel, the ionic current flow is reduced for a time that is proportional to the size of the chain, allowing its length to be easily derived.
If a chain is long enough to reach the narrowest part of the nanopore-known as the pinch point-the force of the electrical field behind it will push the molecule on through the rest of the channel. Exploiting this characteristic, the NIST/Maryland team developed a DNA probe method to measure the distances from the openings on each side of the membrane to the pinch point, and in turn, the entire length of the nanopore by adding the two measurements together. The probes consist of DNA strands of known lengths topped on one end by a polymer sphere. The sphere prevents the probe from completely moving through the nanopore while leaving the DNA chain dangling from it free to extend into the channel. If the chain reaches the pinch point, the force that would normally drive a free DNA chain past the junction instead holds the probe in place (since the polymer sphere "locks" it at the other end) and defines the distance to the pinch point. If the chain is shorter than the distance to the pinch point, it will be bounced out of the nanopore, telling researchers that a longer-length chain is needed to measure the distance to the gap.
The NIST/Maryland researchers also developed a second means of measuring the length of the nanopore to confirm the results of the "single lollipop" method. In this system, polymer molecules are allowed to circulate freely in the solution found on the inner side of the membrane. Polymer-capped DNA probes of different lengths are forced one at a time into the nanopore from the opposite side. If the end of a probe's chain is long enough to completely transverse the channel, it will grab hold of a free polymer molecule in solution. This defines the length of the channel.
Additionally, this "ice fishing" method provides insight into the structure of the nanopore. As the DNA chain winds its way through, changes in electrical voltage correspond to the changing shape of the channel. This information can be used to effectively map the passageway.
* S.E. Henrickson, E.A. DiMarzio, Q. Wang, V.M. Stanford and J.J. Kasianowicz. Probing single nanometer-scale pores with polymeric molecular rulers. The Journal of Chemical Physics 132, 135101 (published online April 2, 2010).
** Alpha-hemolysin, produced by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria