Aug 2 2019
A new technology that could see tyres generate electricity whilst driving is being developed by engineers in Japan. Falken’s parent company, Sumitomo Rubber Industries, together with Professor Hiroshi Tani of Kansai University, have developed the Energy Harvester that takes advantage of the build up of static electricity, known as frictional charging, to produce power efficiently as the tyre turns.
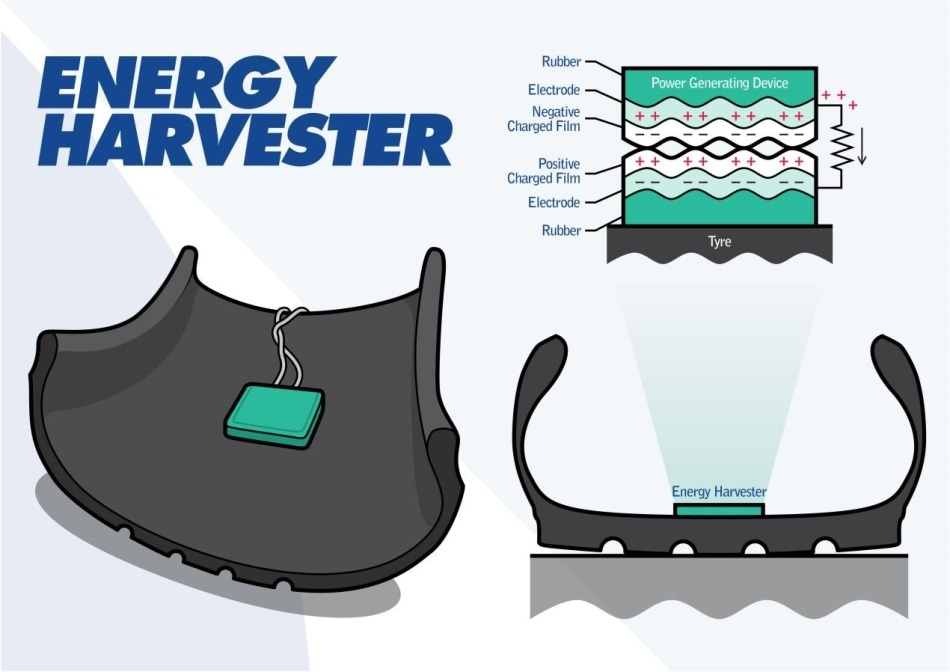
Inside the Energy Harvester are two layers of rubber each covered in an electrode, along with a negatively charged film that interfaces with a positively charged film. When fixed to the inside of a conventional tyre carcass it generates electricity as the tyre deforms during rotation.
Engineers believe the Energy Harvester could lead to practical applications as a power source for sensors used in TPMS (Tyre Pressure Monitoring Systems) and other automotive devices without the need for batteries.
It was created as part of Sumitomo’s R&D programme to develop technologies that target improvements in safety and environmental performance. Now, the research has been selected by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (a national research and development agency) as a Type FS* Seed Project under A-STEP (Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-Driven R&D). Sumitomo Rubber Industries will now advance this research with support from the Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Note - *A programme supporting research and development projects undertaken jointly by academia and enterprise in order to perform feasibility and application studies based on the results of academic research related to technological "seeds," with the ultimate aim of producing new core technologies.