Reviewed by Alex SmithAug 26 2021
The electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2), or CO2ER, provides an ideal path for realizing green CO2 cycling and mitigating the greenhouse effect. A majority of the studies on CO2ER in the recent past have focused on the inherent performance of the catalysts.
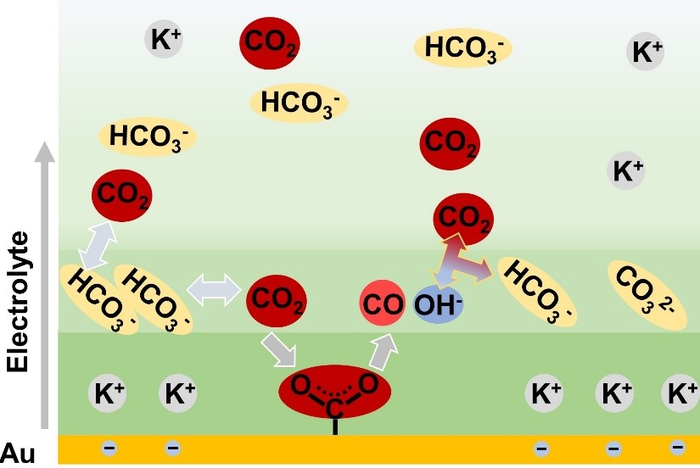 Reduction process of CO2 in CO2-saturated KHCO3 solution over Au catalyst. Wangyu Deng.
Reduction process of CO2 in CO2-saturated KHCO3 solution over Au catalyst. Wangyu Deng.
In general, bicarbonate — an electrolyte or negatively charged ion used by the body to help maintain its pH balance — is used in CO2ER. However, a group of researchers from China set out to perform an investigation of its role and behavior. The findings have been reported in the KeAi journal Fundamental Research.
Bicarbonate, as a common electrolyte anion, can enhance CO2ER activity via its rapid equilibrium exchange with dissolved CO2. We found that higher concentrations of bicarbonate in the electrolyte provided higher energy efficiency.
Jinlong Gong, Study Corresponding Author and Professor, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University
According to Dr. Wanyu Deng, the lead author of the study, “The new knowledge gained in this work guides the direct electroreduction of bicarbonate and provides valuable insights into CO2ER with high-concentration electrolytes. This finding is expected to help save abundant energy in the CO2ER process and can pave the way for advancing the progress of CO2ER towards commercialisation.”
The researchers performed in-situ experimental observations and found an accumulation of negatively charged bicarbonate anions close to the electrode surface. The enriched bicarbonate anions transformed into CO2 to offer reactants.
Moreover, the local concentration of bicarbonate anions was regulated by both the bulk concentration of bicarbonate electrolyte and the cathodic potential. This finding helped account for the dependency of CO2ER activity on the local bicarbonate concentration, where the limited cathodic potential led to a plateau in the CO2ER activity.
This hinders the use of high-concentration electrolytes to enhance activity. Further research is required to systematically explore the intrinsic relationship between CO2ER activity and bicarbonate concentration to achieve better CO2ER performance.
Jinlong Gong, Study Corresponding Author and Professor, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University
Journal Reference:
Deng, W., et al. (2021) Effect of bicarbonate on CO2 electroreduction over cathode catalysts. Fundamental Research. doi.org/10.1016/j.fmre.2021.06.004.