 By Surbhi JainReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.May 4 2022
By Surbhi JainReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.May 4 2022In an article recently published in the open-access journal Energies, researchers discussed the trends in building pumps as well as the perspectives on the advancement of industry 4.0 technologies applied to water pumping systems.

Study: Perspectives on the Advancement of Industry 4.0 Technologies Applied to Water Pumping Systems: Trends in Building Pumps. Image Credit: buffaloboy/Shutterstock.com
Background
The desire for efficiency in water and energy use has been crucial for human growth from ancient times. High energy demand has become one of the solutions to building verticalization, as there exists a direct relationship between population density, building height, and the pumping system. To effectively integrate important equipment into residential buildings, these systems must have low rates of failure and should be efficient.
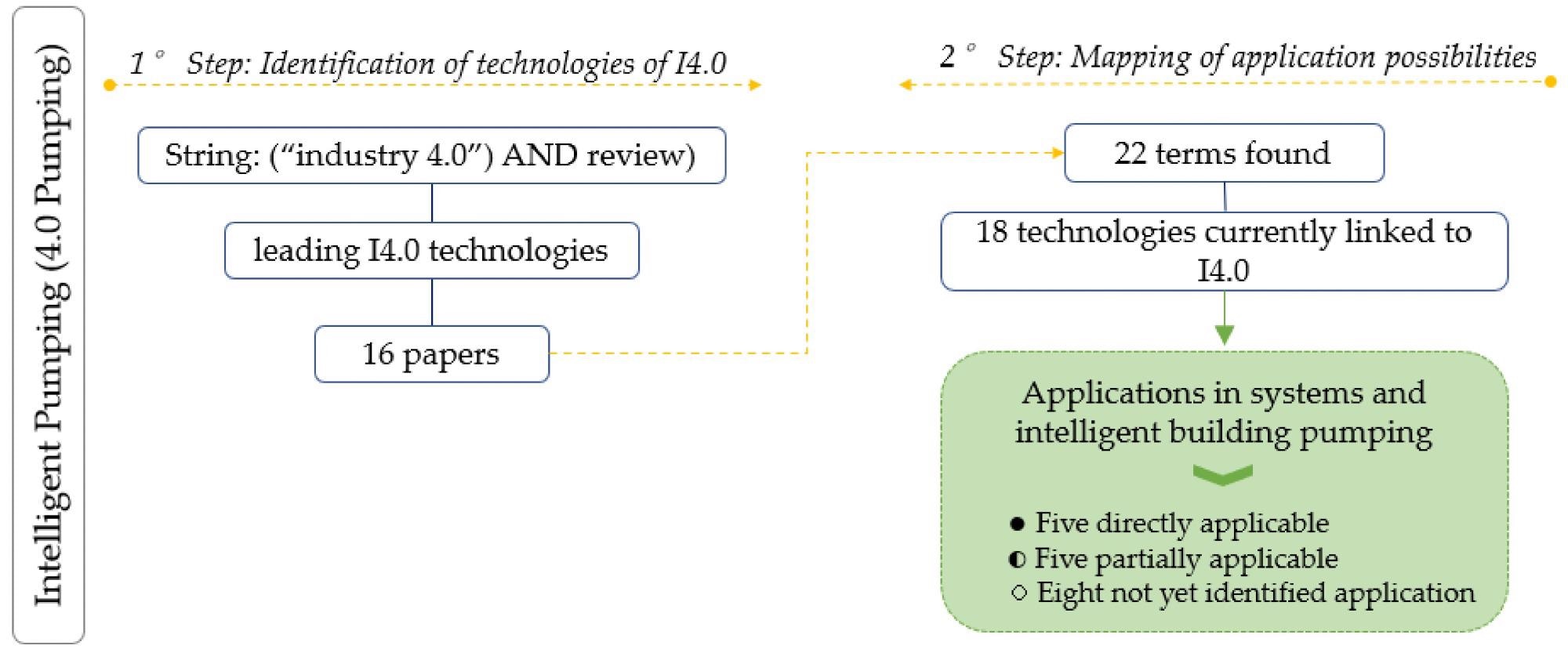
Flowchart of the methodological steps of the study. Image Credit: de Souza, D. F et al., Energies
The Minimum Energy Performance Standard (MEPS), as well as equipment efficiency labels, are two indicators for improving pumping system energy efficiency. The equipment with the greatest decrement in the energy losses associated with the pumping systems is hydraulic pumps and electric motors. However, owing to the theoretical limitations of the technologies, the efficiency indicators of this equipment tend to stabilize.
Industrial process management has changed significantly as a result of Industry 4.0 (I4.0) technologies, with a strong trend toward computerization of product manufacturing and manufacturing processes, as well as concepts of efficiency, safety, and sustainability, to be in accordance with the need to improve the efficiency of water pumping systems.
About the Study
In this study, the authors discussed the use of I4.0 technologies in building water pumping systems, with an emphasis on energy efficiency, pump supervision, and control. Four steps were considered in the project in which existing I4.0 technologies were recognized, and the possibilities for using I4.0 technologies in the construction of pumping systems were mapped. Sixteen articles published in journals between 2018 and June 2021 were examined in order to find the I4.0 technologies mentioned in the articles.
The researchers recognized and grouped 18 technologies based on 22 phrases found in the papers. The recognized technologies were categorized into three probable uses in a building water pumping system. The primary focus was to find out what technologies should be included in building water pumping systems in order for them to be considered intelligent pumping. The possible applications of I4.0 technologies for water pumping systems in buildings were mapped to provide a flexible architecture for the desired application.
The proposed methodology entailed the identification of the leading I4.0 technologies and the mapping of the I4.0 technologies' application possibilities. Traditional pumping systems were engaged when there was a lower amount of water in the upper reservoir unit and a comparatively higher amount of water in the lower reservoir unit.
![PF curve represents the condition of a component until functional failure. Source: Adapted from [52].](https://d12oja0ew7x0i8.cloudfront.net/images/news/ImageForNews_58985_16516617084747571.jpg)
PF curve represents the condition of a component until functional failure. Image Credit: de Souza, D. F et al., Energies
The team discussed how to incorporate the leading I4.0 technologies in a pumping system so that it could be deemed intelligent pumping (4.0 pumping) in a building system. The classification options for I4.0 technology were determined to increase the user connectivity, the useful life of the water pumping system, and the construction of the pumping system with high energy efficiency.
Observations
With the use of variable speed drives (VSDs) in electric motors that drive hydraulic pumps to pump water, considerable productivity benefits were associated with a total of 20 to 40% energy consumption, 53% fewer breakdowns, an average 38% water leakage reduction, and longer motor pump life. The building water pumping system was an essential component of the services required for the buildings to function properly.
Intelligent sensors, cloud, and edge computing, big data & data mining, internet of things (IoT), machine learning and artificial intelligence, human-machine interface (HMI), cyber security, and systems integration and network operation were identified as the leading I4.0 technologies, which were mapped in selected papers and their application possibilities discussed in relation to building pumping systems.
The use of I4.0 technologies to create intelligent pumping systems would reduce water loss, waste, user control, and service continuity, which could result in a more adaptable and intelligent pumping system. Smart sanitation was a critical component of the development of smart cities. However, progress toward intelligent building systems was required, which boosted the use of big data, IoT, intelligent sensors, and other technologies. This avalanche of data opened up new possibilities for water design and management in buildings, as well as new business opportunities.
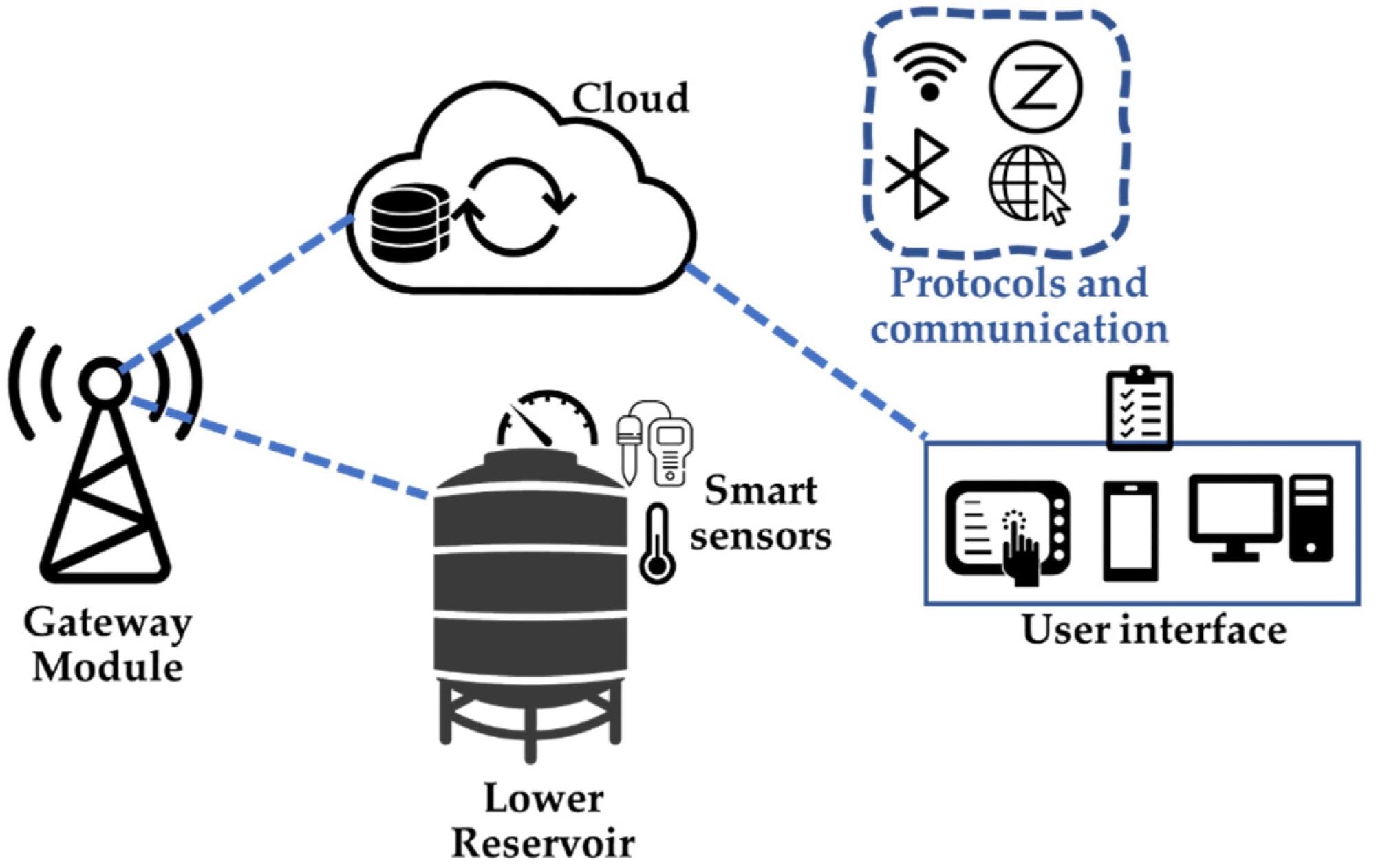
Simplified schematic of the IoT process for water quality monitoring. Image Credit: de Souza, D. F et al., Energies
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study looked at some of the I4.0 technologies that are already being employed in building water pumping systems. The majority of pumping system research focused on heat pumps, water supply, and irrigation systems in agriculture. The study highlighted the benefits of I4.0 technologies, which were originally designed for the industrial sector but are now also suitable for residential building water pumping systems. The contemporary concept of I4.0 and the vast areas of application were demonstrated in this study.
The authors believe that to drive the adoption of smart building systems in the real world, better coordination between academia, business, and the government is crucial.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
de Souza, D. F., da Guarda, E. L. A., da Silva, W. T. P., et al. Perspectives on the Advancement of Industry 4.0 Technologies Applied to Water Pumping Systems: Trends in Building Pumps. Energies 15(9) 3319 (2022). https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/9/3319