Green construction adoption has become essential to guarantee environmental sustainability. The most recent research in the journal Energies uses an analytical hierarchy process to include a detailed state-of-the-art evaluation on enhancing existing methodologies in sustainable architecture/building.

Study: Opportunities for Using Analytical Hierarchy Process in Green Building Optimization. Image Credit: Olga Kashubin/Shutterstock.com
Advancements in Energy Efficient Buildings
Construction residents have expected to live in building structures that offer an adaptable, pleasant, and energy-efficient lifestyle at a minimal price. Numerous unique design techniques have been implemented to achieve this goal, enhance the efficiency of buildings, and meet a variety of human needs as well as ecological sustainability.
Furthermore, AHP's underlying ability to deal with various decision-making styles, where it has typically been implemented in its innovation, has become its executive scientific goal over the last few years.
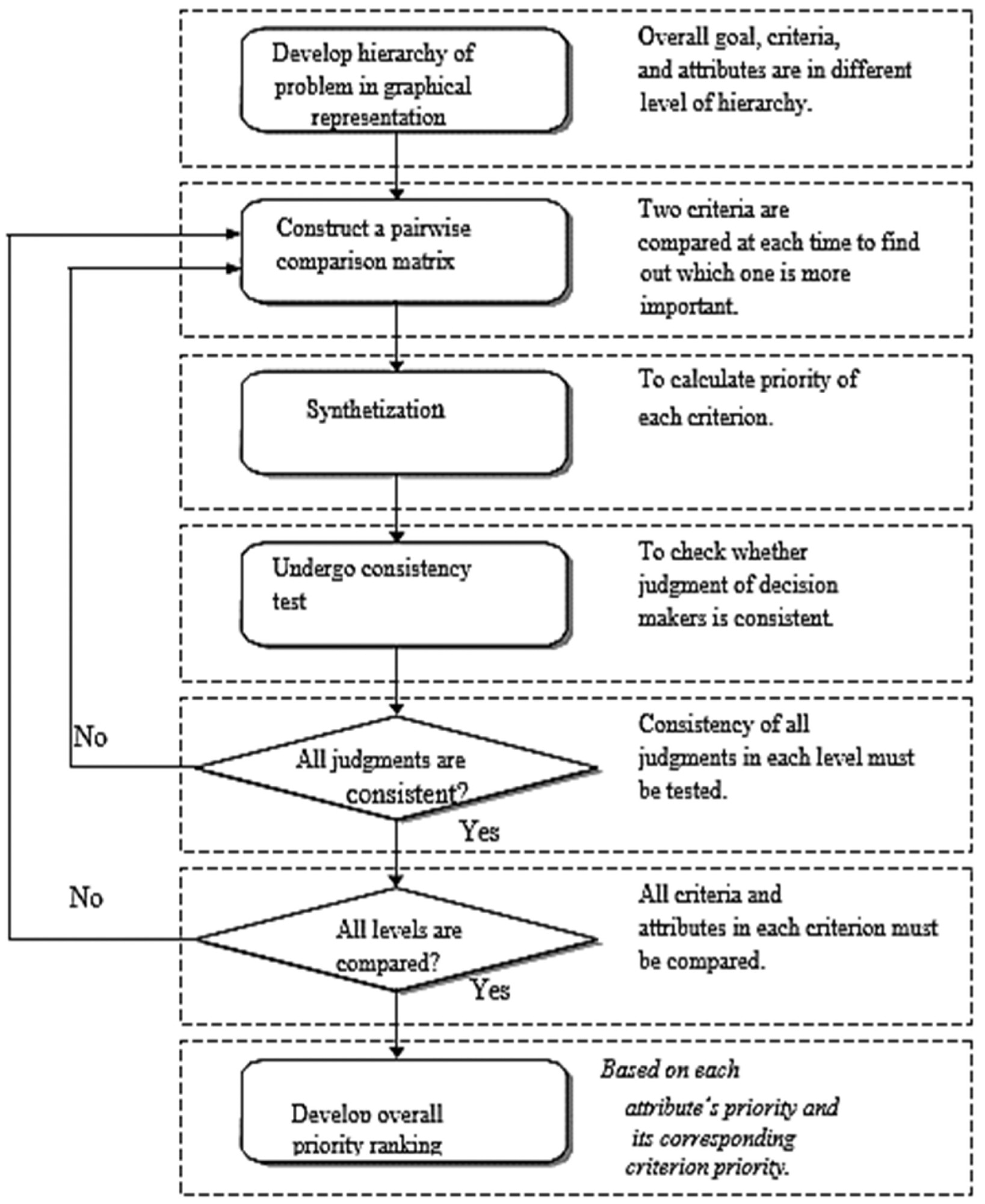
The analytic hierarchy process flowchart. Image Credit: Elshafei G et al., Energies
What is Green Plan for Ecological Architecture?
The eco-systemic architectural ecofriendly strategy can be defined as the discovery of solutions to many interconnected factors such as self-sustaining renewable electricity, smudging configuration, photovoltaics, sewage disposal, and double-skin exteriors and soundproofing for building structures. These would not only cooperate with engineering standards and maximize work efficiency based on design priorities but would also meet usefulness and aesthetic requirements.
Which Elements Play a Crucial Role in Sustainable Building?
It is essential to identify a productive maintenance and rehabilitation strategy that mimics the decision maker's goals to help achieve the goal of zero-energy constructions.
Another critical factor is developing criteria to rank some markers depending on the level of importance in order to solve energy-saving issues, as well as predicting a comprehensive measure that represents all perspectives in the building manufacturing procedure in order to produce fit and error-free buildings.
Developing an internet-based policy for sustainable buildings to investigate the characteristics of any progress stage in architectural design is also critical.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Modern Digital Technologies
In rejuvenation and urban planning, the prospective use of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, devices, and knowledge in management information systems is well understood.
Concerns have been raised, however, while beginning efforts for recovery planning within inhabited fabricated circumstances, resulting in an increased level of natural adversity and financial effects from the conventional local area. With the advancement of high-speed internet innovations, more advanced AI techniques, and diagrammatical digitization, the realm of spatial analysis and improvement has become a major area of research.
What is the AHP Technique?
The AHP is a decision-making method with several parameters. At different phases, it employs a hierarchal structure of prerequisites, sub-criteria, preferences, and possibilities. The AHP's primary operations include hierarchy construction, prioritized evaluation, and reliability testing.
Following that, decision-makers must divide particular assessment challenges with varying factors into sections with potential characteristics organized at numerous levels of hierarchy. The decision-makers must then make a comparison of each group at the same phase in a pair-wise manner based on skills and awareness.
The final method is termed consistency confirmation, and it is regarded as one of the most advantageous aspects of the AHP because it is used to guarantee that the results are consistent.
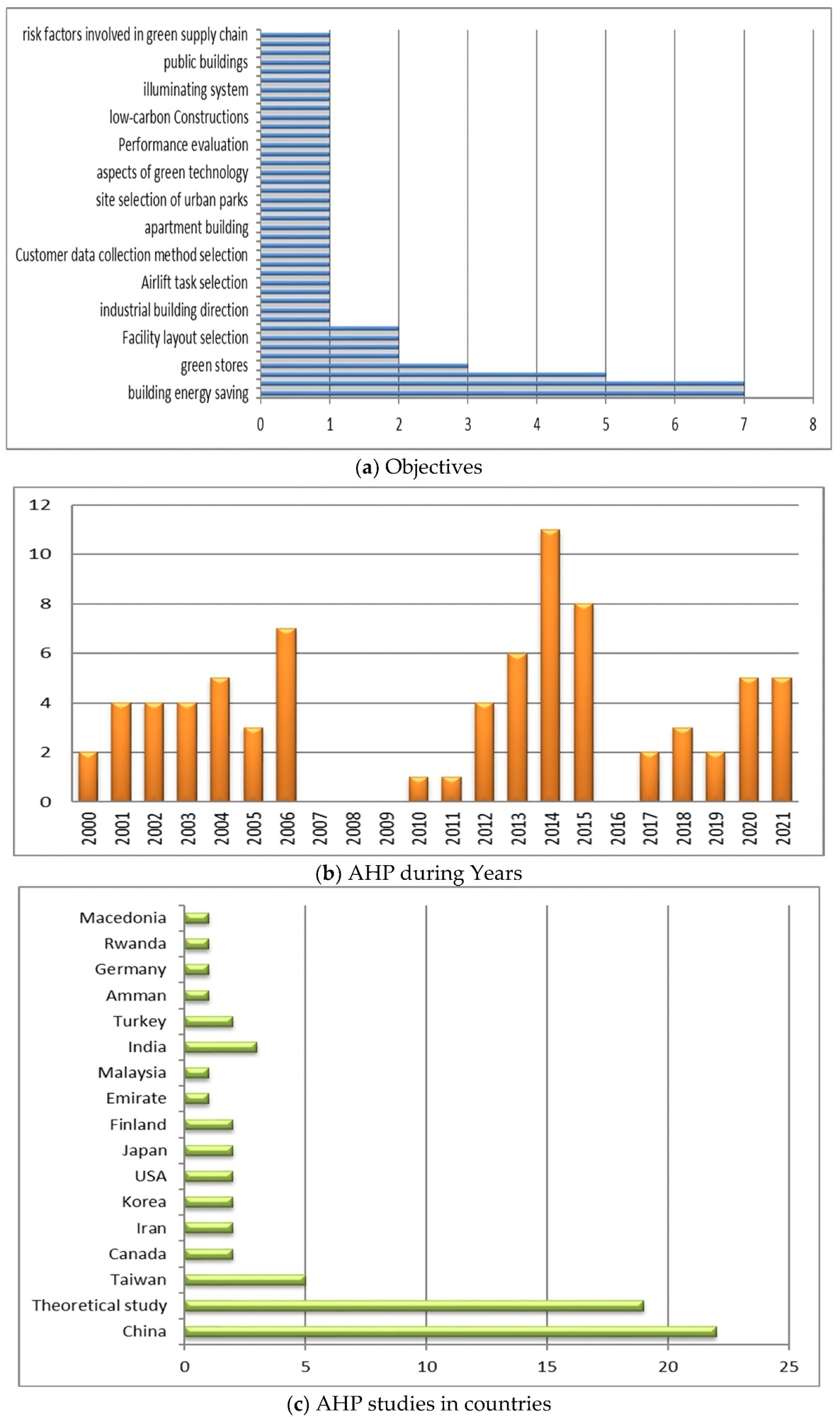
AHP graphical information (a) AHP objectives, (b) the AHP during years, (c) the AHP studies in countries, (d) the AHP and its combination schemes and (e) AHP Applications. Image Credit: Elshafei G et al., Energies
Goal Programming Model (GP)
A specialized goal programming (GP) model has also been established as a decision-making approach for measuring the necessities of goals and weights of variance factors to confront the multi-target problem with the conjunction of non-relaxation implications and relaxation restrictions.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
To strengthen an office territory judgment based on need, AHP and quality function deployment (QFD) methods are suggested. The technique began by identifying area requirements, then deriving area evaluating standards, and finally constructing a focal relationship lattice to demonstrate the degree of relationship between each set of region necessities and area framework for the QFD process.
AHP and SWOT Analysis
A centralized AHP approach with strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) has also been suggested to aid decision-making in a Finnish ranger service.
In addition, it has been integrated with many other techniques for gathering accurate analysis and results.
Future Perspective
In the future, it would be beneficial to consider some of the impending AHP applications that could aim to build expertise management frameworks in order to find new techniques required for building comprehension techniques in green building development.
Further Reading
Elshafei G et al. (2022). Opportunities for Using Analytical Hierarchy Process in Green Building Optimization. Energies. 15(12). 4490. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/12/4490
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.