The ever-increasing demand for the integration of micro/nanosystems, such as MEMS, micro/nanorobots, intelligent portable/wearable microsystems, as well as implantable miniaturized medical devices, has accelerated the development of precise miniaturized energy storage devices (MESDs) and their intense manufacturing processes.
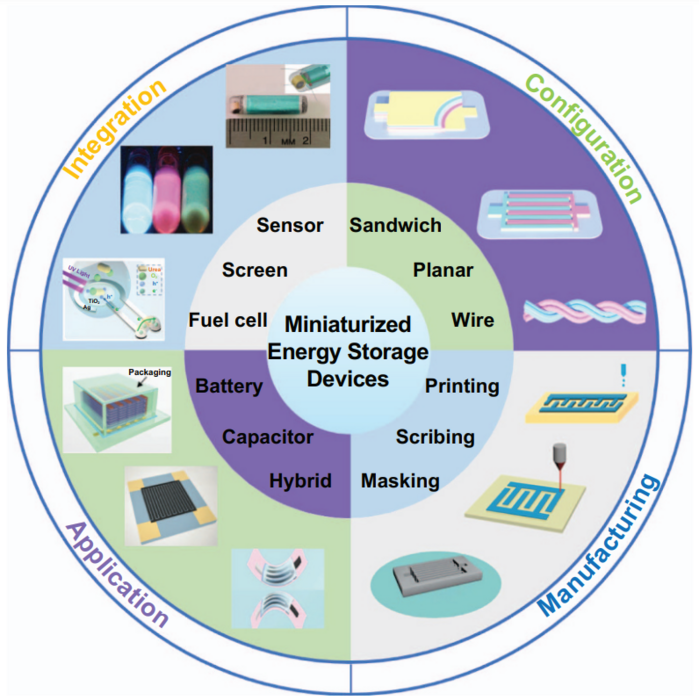 Configuration design, microelectrode manufacturing, typical applications, and on-chip integrated microsystems. Image Credit: Huaizhi Liu, Guanhua Zhang, Xin Zheng, Fengjun Chen, Huigao Duan.
Configuration design, microelectrode manufacturing, typical applications, and on-chip integrated microsystems. Image Credit: Huaizhi Liu, Guanhua Zhang, Xin Zheng, Fengjun Chen, Huigao Duan.
MESDs are typically a type of miniaturized power supply with electrode sizes in the micrometer range that not only serve as a compatible energy source for micro/nanosystems but also directly integrate with micro/nanodevices to meet the need for integration, intelligence, ultra compactness, and exceptionally lightweight. As a result, MESDs are regarded as superior compact energy sources for the continuous powering of integrated microsystems.
A group of researchers headed by Dr. Huigao Duan and Dr. Guanhua Zhang from the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and Manufacturing for Vehicle Body, College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering, Hunan University, People’s Republic of China, offered a complete analysis of the history, basics, device configurations, manufacturing methods, and typical applications of MESDs in a recent study published in the International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing. Furthermore, current breakthroughs in MESDs and their functional integration are comprehensively described.
This study focused on on-chip integrated microsystems, which include miniature energy storage units and a variety of useful micro electrical devices. Finally, the authors proposed a new avenue for advancing the research and practical implementation of miniaturized energy storage devices and integrated microsystems.
Classic micro batteries (MBs), micro-supercapacitors (MSCs), and recently created micro hybrid metal ion capacitors (MHMICs) are all examples of MESDs.
MESDs, in particular, are preferred for powering miniaturized, flexible/wearable electronics and integrated micro/nanosystems due to their compact size, compatible performance, and ability to satisfy intense customizable requirements, such as achieving high output voltage (in series), high output current (in parallel), as well as high output power (multiple series).
Furthermore, MESDs are the most hopeful candidate for a power supply with an inseparable position as power storage components for miniaturized electronic devices and integrated microsystem applications due to their ease of integration with specific microelectronic devices on a compliant substrate.
The on-chip integration of specific functions into MESDs can give them more impressive properties, making them acceptable and accessible for microsystem applications. An optimal on-chip integrated system that relies on MESDs should not only have excellent electrochemical performance and endurance but should also have the necessary attributes for particular applications.
MESDs combined with energy harvesters, screen displays, transmitters, fuel cells, and functional electronics such as electrochromic and various sensors have been intensively explored in this sector and seem to have potential future use in integrated microsystems.
From current MESD advancements and successes, it is worth highlighting that the challenges are not only to improve electrochemical characteristics, such as high energy density and high power density in a small footprint with a long lifespan, but also to integrate with multifunctional features, matching up with many of the requirements of microelectronic devices and microsystems.
Mr. Huaizhi Liu, Dr. Guanhua Zhang, Dr. Huigao Duan, et al. recognized the following significant difficulties in future research to better support the development of MESDs:
- High-performance, multifunctional active materials for microelectrodes are being investigated
- Creating microelectrode manufacturing methods that are simple to use, low-cost, time-saving, extremely safe, environmentally friendly, and scalable
- Optimizing device setup and the complicated links between structural design, electrolyte selection, and electrochemical property
- Developing self-powered, multifunctional on-chip integrated microsystems that include energy harvesting, storage, and consumption devices
Despite the promising prospects, researchers must continue to investigate new avenues to better the development and application of MESDs. Engineers must identify practical applications for them, such as wearable gadgets, implanted devices, and micro/nano systems. While there is still a long way to go before it becomes a reality, the potential of MESDs is incredibly promising.
Journal Reference:
Liu, H., et al. (2022) Emerging miniaturized energy storage devices for microsystem applications: from design to integration. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing. doi.org/10.1088/2631-7990/abba12.