Epoxy resin monomers used in industry can cause severe contact allergies. However, a new type of epoxy resin monomer that is considerably less allergenic and based on a renewable material has been created by researchers at the University of Gothenburg.
 Epoxy resin monomers used in industry can cause severe contact allergies. However, researchers at the University of Gothenburg have created a new type of epoxy resin monomer that is considerably less allergenic and based on a renewable material.
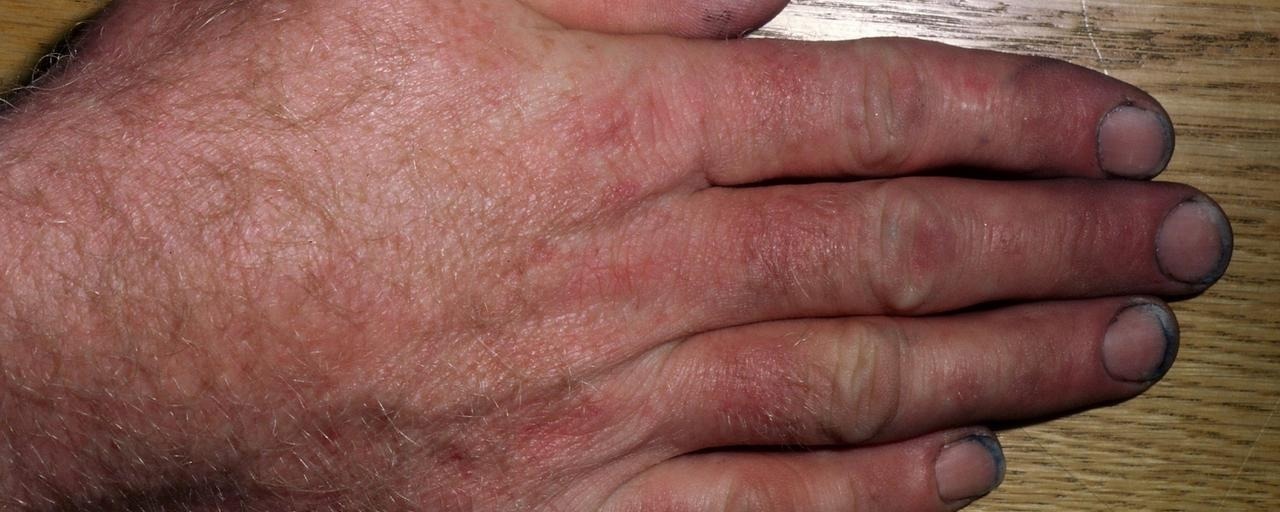
Epoxy resin monomers used in industry can cause severe contact allergies. However, researchers at the University of Gothenburg have created a new type of epoxy resin monomer that is considerably less allergenic and based on a renewable material.
The epoxy resin monomers used today contain residues of the endocrine disruptor Bisphenol A (BPA). However, the novel monomer derived from ordinary sugar is not based on BPA.
Epoxy resin monomers have long been employed in the construction industry, and more recently, they have been used to create the plastics used in wind turbines. BPA, which is made from petroleum, is used to make the monomer.
The risk of developing a contact allergy when handling epoxy resin monomers is quite high, and sometimes wearing protective clothing is not enough.
When we started our research, we had three goals. The monomer should be far less allergenic, be based on an easily accessible and renewable starting material, and not based on BPA, which is a known endocrine disruptor.
Kristina Luthman, Professor, Medicinal Chemistry, University of Gothenburg
Residues Remain in the Polymer
Epoxy resin polymers are formed by allowing two substances to react with each other. One of these substances, called DGEBA (Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether), is reactive and helps to produce durable and cured plastics.
However, even after curing, the epoxy resin polymer still contains traces of the endocrine disruptor BPA and the contact allergen DGEBA, which pose health hazards.
A novel epoxy resin monomer has been created by researchers at the University of Gothenburg based on isosorbide, a substance made from glucose or ordinary sugar. The people who work with epoxy resin monomers will benefit the most from this study.
Luthman added, “If the monomer is less allergenic, this is of great practical importance. It may then be enough to wear protective clothing, which is not always the case today.”
Cheap Input Material
Another advantage of the new substance is that it is created from a renewable starting material (sugar beet) rather than fossil oil, as are most epoxy resin monomers today.
The produced monomer will next be examined to see if it has the necessary qualities to replace the epoxy resin monomers currently used in industrial applications. The material is less expensive since it is made from sugar.
“Usability and cost-effectiveness will be questions for the plastics industry to address. One obstacle is that BPA is cheap and useful for creating plastics with a variety of properties. So, it may be difficult to convince industry to make the switch. But if the use of BPA is regulated more strictly within the EU, that will put the matter in a whole different light,” Luthman concluded.
Journal Reference:
Karlsson, I., et al. (2023) Nature-Derived Epoxy Resin Monomers with Reduced Sensitizing Capacity─Isosorbide-Based Bis-Epoxides. Chemical Research in Toxicology. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00347.