Nov 10 2009
In work that someday may lead to the development of novel types of nanoscale electronic devices, an interdisciplinary team of researchers at the California Institute of Technology has combined DNA's talent for self-assembly with the remarkable electronic properties of carbon nanotubes, thereby suggesting a solution to the long-standing problem of organizing carbon nanotubes into nanoscale electronic circuits.
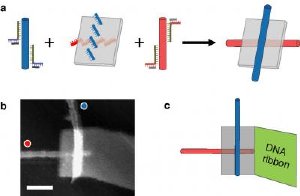 In (a), single-wall carbon nanotubes labeled with "red" and "blue" DNA sequences attach to anti-red and anti-blue strands on a DNA origami, resulting in a self assembled electronic switch. In (b), an atomic force microscopey image of one such structure. The blue nanotube appear brighter because it is on top of the origami; the red nanotube sits below. Scale bar is 50 nm. In (c), a diagrammatic view of the structure shown in b. The gray rectangle is the DNA origami. A self-assembled DNA ribbon attached to the origami improves structural stability and ease of handling. Credit: Paul W. K. Rothemund, Hareem Maune, and Si-ping Han/Caltech/Nature Nanotechnology.
In (a), single-wall carbon nanotubes labeled with "red" and "blue" DNA sequences attach to anti-red and anti-blue strands on a DNA origami, resulting in a self assembled electronic switch. In (b), an atomic force microscopey image of one such structure. The blue nanotube appear brighter because it is on top of the origami; the red nanotube sits below. Scale bar is 50 nm. In (c), a diagrammatic view of the structure shown in b. The gray rectangle is the DNA origami. A self-assembled DNA ribbon attached to the origami improves structural stability and ease of handling. Credit: Paul W. K. Rothemund, Hareem Maune, and Si-ping Han/Caltech/Nature Nanotechnology.
A paper about the work appeared November 8 in the early online edition of Nature Nanotechnology.
"This project is one of those great 'Where else but at Caltech?' stories," says Erik Winfree, associate professor of computer science, computation and neural systems, and bioengineering at Caltech, and one of four faculty members supervising the project.
Both the initial idea for the project and its eventual execution came from three students: Hareem T. Maune, a graduate student studying carbon nanotube physics in the laboratory of Marc Bockrath (then Caltech assistant professor of applied physics, now at the University of California, Riverside); Si-ping Han, a theorist in materials science who is investigating the interactions between carbon nanotubes and DNA in the Caltech laboratory of William A. Goddard III, Charles and Mary Ferkel Professor of Chemistry, Materials Science, and Applied Physics; and Robert D. Barish, an undergraduate majoring in computer science who was working on complex DNA self-assembly in Winfree's lab.
The project began in 2005, shortly after Paul W. K. Rothemund invented his revolutionary DNA origami technique. At the time, Rothemund was a postdoctoral scholar in Winfree's laboratory; today, he is a senior research associate in bioengineering, computer science, and computation and neural systems.
Rothemund's work gave Maune, Han, and Barish the idea to use DNA origami to build carbon nanotube circuits.
DNA origami is a type of self-assembled structure made from DNA that can be programmed to form nearly limitless shapes and patterns, such as smiley faces or maps of the Western Hemisphere or even electrical diagrams. Exploiting the sequence-recognition properties of DNA base paring, DNA origami are created from a long single strand of viral DNA and a mixture of different short synthetic DNA strands that bind to and "staple" the viral DNA into the desired shape, typically about 100 nanometers (nm) on a side.
Single-wall carbon nanotubes are molecular tubes composed of a rolled-up hexagonal mesh of carbon atoms. With diameters measuring less than 2 nm and yet with lengths of many microns, they have a reputation as some of the strongest, most heat-conductive, and most electronically interesting materials that are known. For years, researchers have been trying to harness their unique properties in nanoscale devices, but precisely arranging them into desirable geometric patterns has been a major stumbling block.
"After hearing Paul's talk, Hareem got excited about the idea of putting nanotubes on origami," Winfree recalls. "Meanwhile, Rob had been talking to his friend Si-Ping, and they independently had become excited about the same idea."
Underlying the students' excitement was the hope that DNA origami could be used as 100 nm by 100 nm molecular breadboards-construction bases for prototyping electronic circuits-on which researchers could build sophisticated devices simply by designing the sequences in the origami so that specific nanotubes would attach in preassigned positions.
"Before talking with these students," Winfree continues, "I had zero interest in working with carbon nanotubes or applying our lab's DNA-engineering expertise toward such practical ends. But, seemingly out of nowhere, a team had self-assembled with a remarkable spectrum of skills and a lot of enthusiasm. Even Si-Ping, a consummate theorist, went into the lab to help make the idea become reality."
"This collaborative research project is evidence of how we at Caltech select the top students in science and engineering and place them in an environment where their creativity and imagination can thrive," says Ares Rosakis, chair of the Division of Engineering and Applied Science at Caltech and Theodore von Kármán Professor of Aeronautics and professor of mechanical engineering.
Bringing the students' ideas to fruition wasn't easy. "Carbon nanotube chemistry is notoriously difficult and messy-the things are entirely carbon, after all, so it's extremely difficult to make a reaction happen at one chosen carbon atom and not at all the others," Winfree explains.
"This difficulty with chemically grabbing a nanotube at a well-defined 'handle' is the essence of the problem when you're trying to place nanotubes where you want them so you can build complex devices and circuits," he says.
The scientists' ingenious solution was to exploit the stickiness of single-stranded DNA to create those missing handles. It's this stickiness that unites the two strands that make up a DNA helix, through the pairing of DNA's nucleotide bases (A, T, C, and G) with those that have complementary sequences (A with T, C with G).
"DNA is the perfect molecule for recognizing other strands of DNA, and single-stranded DNA also just happens to like sticking to carbon nanotubes," says Han. "So we mix bare nanotubes with DNA molecules in salt water, and they stick all over the nanotubes' surfaces. However, we make sure that a little bit of each DNA molecule is protected, so that that little portion doesn't stick to the nanotube, and we can use it to recognize DNA attached to the DNA origami instead."
The scientists created two batches of carbon nanotubes labeled by DNA with different sequences, which they called "red" and "blue."
"Metaphorically, we dipped one batch of nanotubes in red DNA paint, and dipped another batch of nanotubes in blue DNA paint," Winfree says. Remarkably, this DNA paint acts like color-specific Velcro.
"These DNA molecules served as handles because a pair of single-stranded DNA molecules with complementary sequences will wrap around each other to form a double helix. Thus," he says, "red can bind strongly to anti-red, and blue with anti-blue."
"Consequently," he adds, "if we draw a stripe of anti-red DNA on a surface, and pour the red-coated nanotubes over it, the nanotubes will stick on the line. But the blue-coated nanotubes won't stick, because they only stick to an anti-blue line."
To make nanometer-scale electronic circuits out of carbon nanotubes requires the ability to draw nanometer-scale stripes of DNA. Previously, this would have been an impossible task. Rothemund's invention of DNA origami, however, made it possible.
At this point, the researchers were confident that they had created a method that could construct a device from a mixture of nanotubes and origami.
"It worked," Winfree says. "I can't say perfectly-there's lots of room for improvement. But it was sufficient to demonstrate the controlled construction of a simple device, a cross-junction of a pair of carbon nanotubes."