Feb 12 2016
Purdue University researchers have shown that a synthetic version of a high-strength adhesive produced by mussels is non-toxic to living cells, suggesting its potential suitability for surgical and other biomedical applications.
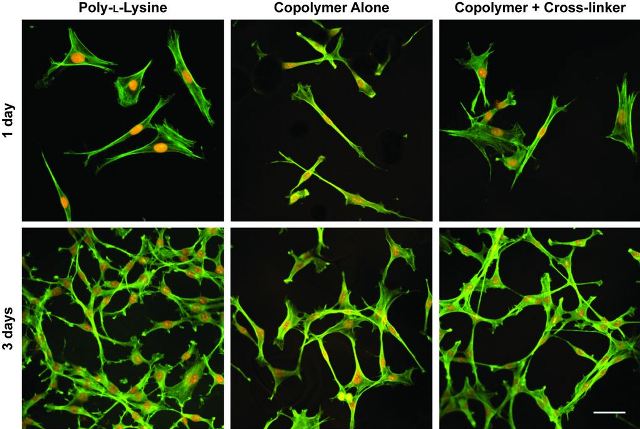 A synthetic version of a high-strength adhesive produced by mussels has been shown to be non-toxic to living cells. Cells cultured on a control polymer, at left, the new synthetic polymer, center, and the new polymer reinforced through "cross-linking” were shown to have their normal shape and structure after one and three days. (Purdue University image/ M. Jane Brennan, Heather J. Meredith and Courtney L. Jenkins)
A synthetic version of a high-strength adhesive produced by mussels has been shown to be non-toxic to living cells. Cells cultured on a control polymer, at left, the new synthetic polymer, center, and the new polymer reinforced through "cross-linking” were shown to have their normal shape and structure after one and three days. (Purdue University image/ M. Jane Brennan, Heather J. Meredith and Courtney L. Jenkins)
“One long-term goal is to potentially replace sutures and screws owing to the trauma caused from punching holes into healthy tissue. These classic methods to join tissue also concentrate mechanical stresses on the tissues as well as creating sites for infection,” said Jonathan Wilker, a professor of chemistry and materials engineering who helped lead a research team that developed the polymer. “A possibly improved approach would be to use adhesives for connecting tissues.”
In new findings, researchers have shown the polymer, poly[(3,4-dihydroxystyrene)-co-styrene], is non-toxic to cells, said Julie Liu, an associate professor of chemical engineering and biomedical engineering who co-led the study.
The polymer, which the researchers have named catechol-polystyrene, is designed after a natural protein that mussels produce for sticking to surfaces. The animals extend hair-like fibers that connect to surfaces with a natural adhesive. A synthetic polymer is needed because the natural proteins are not practical for industrial applications.
“We designed this polymer to be a mimic of the natural proteins,” Wilker said. “It can be stronger than Super Glue under some conditions. You can also get the polymer to set completely underwater, which is not too common for most adhesives.”
The researchers tested the polymer with mouse cells called NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. These cells are often used in research to assess toxicity by examining how well cells survive and grow when exposed to new materials.
The findings were detailed in a research paper that appeared online in January in the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A. The paper also was authored by graduate students M. Jane Brennan, Heather J. Meredith and Courtney L. Jenkins.
“We are trying to assess whether the glue is toxic or tolerated well by the cells,” Liu said.
Tests using two types of assays revealed that the cells continue to function properly when exposed to the polymer. In one of the assays, the cells with intact membranes produce a key enzyme, which indicates that they are alive.
“We are not yet at the point where we can claim bio-compatibility,” Liu said. “At this stage, we are providing the first step to show that this polymer system does not seem to affect cell response. We are asking the questions – do the cells live, do they divide, do they change shape? All indications are very good so far.”
The polymer contains “pendant groups” that dangle from the central backbone and are similar to such groups in the natural proteins.
“The polymer is a simplified version of the proteins made by mussels for adhesion,” Wilker said.
Future research will include developing next-generation adhesive materials and performing tests with tissue specimens.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation (Awards DMR-1309787 and CHE-0952928 and a Graduate Fellowship), 3M Nontenured Faculty Award, a Steven C. Beering Fellowship and the Office of Naval Research (Award N00014-13–1-0327).
Writer: Emil Venere, 765-494-4709 FREE, [email protected]
Sources: Julie C. Liu, 765-494-1935 FREE, [email protected]
Jonathan Wilker, 765-496-3382 FREE, [email protected]
Note to Journalists: A copy of the research paper is available from Emil Venere, Purdue News Service, at 765-494-4709 FREE, [email protected]