Jun 4 2018
Chemists have used a novel technique to modify the enzyme levansucrase. This enzyme can now create sugar polymers that hold potential applications in medicine and the food industry.
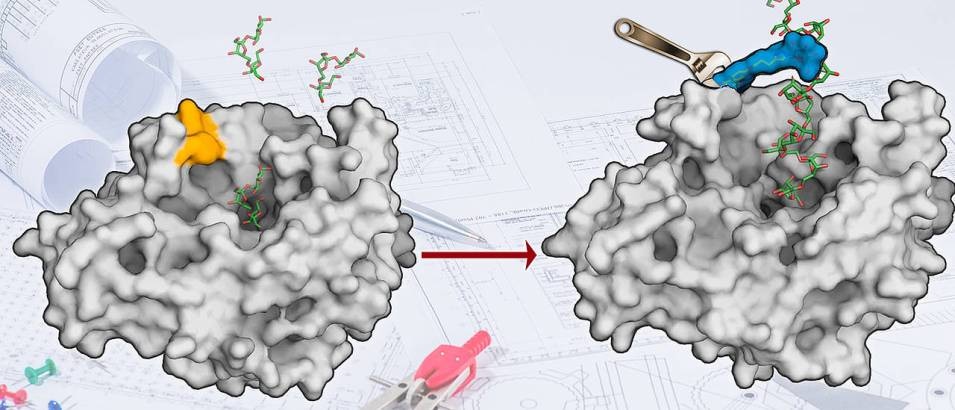 The surface of the enzyme levansucrase has been redesigned to produce sugar polymers. (Picture: AK Seibel)
The surface of the enzyme levansucrase has been redesigned to produce sugar polymers. (Picture: AK Seibel)
Being tools of nature, enzymes function as biological catalysts and speed up nearly all biochemical reactions in living cells. This is the reason why enzymes have been employed in the chemical sector for some time now - in cleaners and detergents, shampoos and toothpastes, and even in food products. In addition, enzymes aid in the production of textiles, paper, medicines, biofuels, leather, and other products.
Enzymes from the tailoring industry
Biochemically, enzymes are essentially proteins that contain natural amino acids and form a three-dimensional structure. Similar to how a key fits into a lock, each particular molecule fits into an enzyme, which changes this molecule into a new product.
Technically, individual amino acids can be exchanged in an enzyme and therefore its structure can be changed to enable it to process other molecules. In this fashion, British researchers have recently produced a mutant enzyme that has the ability to break down plastic.
Surface of the levansucrase changed
At Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany, chemists have now gone one step further in the customization of enzymes, "We thought what fascinating possibilities would arise if we could change the surface of enzymes chemically and use the chemical space of molecules," says Jürgen Seibel, Professor of Organic Chemistry at the JMU. "We have developed a reaction that does not occur in nature in this way. It gives us a lot of freedom in reshaping enzyme surfaces. "
As reported by the JMU researchers in the journal "Chemical Science", they initially reengineered the surface of the levansucrase enzyme and now this enzyme can directly change the table sugar (sucrose) into a polymer of fructose building blocks.
So far, such a synthesis has been possible with levansucrase, but it works much more efficiently with the modified enzyme.
Jürgen Seibel
The conversion of the levansucrase enzyme per second is currently considerably higher; additionally, it chiefly produces the required product without any accidental by-products.
Interesting for medicine and food industry
The fructose polymer can possibly be utilized in the food industry – for instance as a probiotic supplement in baby food or yogurts, or as a bio-gel for tissue transplantation in the medical field. This is because similar to other functional sugars, the fructose polymer may also serve specific intestinal bacteria as food and indirectly induce a health-promoting effect on the humans’ intestinal flora.
“Product-Oriented Chemical Surface Modification of a Levansucrase (SacB) via an Ene-type Reaction”, Maria Elena Ortiz-Soto, Julia Ertl, Jürgen Mut, Juliane Adelmann, Thien Anh Le, Junwen Shan, Jörg Teßmar, Andreas Schlosser, Bernd Engels, Jürgen Seibel. Chemical Science 2018 Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/C8SC01244J