 By Surbhi JainReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.May 24 2022
By Surbhi JainReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.May 24 2022In an article recently published in the open-access journal Energies, researchers discussed the development of solar energy projects and their utilization in and around the United Arab Emirates (UAE).

Study: A Review on Solar Energy Utilization and Projects: Development in and around the UAE. Image Credit: Fit Ztudio/Shutterstock.com
Background
Because of the remarkable progress of the economy and population growth in the UAE, demand for energy has expanded significantly.
Renewable energy resources, which rely on natural resources to provide an endless supply of sustainable and non-polluting energy, are a viable alternative to conventional energy resources which have gained popularity in recent decades as a means of addressing energy shortages. For various reasons, solar energy may be the best option for the future, and photovoltaic devices are usually easy to use and maintain.
In recent years, solar tracking system (ST) technologies have been developed to increase the amount of solar energy harvested from the sun. So far, no comprehensive assessments of solar energy resources have been published in any of the UAE's seven emirates.
About the Study
In this study, the authors discussed five major aspects of solar energy utilization and projects in the UAE, which started with the recent advances in solar scenario and development trends, followed by electricity production, tariffs, and consumption. Various key aspects of photovoltaic solar installation projects inside Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and other smaller projects in the UAE were also discussed.
The team examined the current solar energy research and activities in the UAE in depth. The primary purpose of this research was to build on previous work by providing an overview of the UAE's energy portfolio along with the electricity consumption, production, and pricing in the UAE's seven emirates.
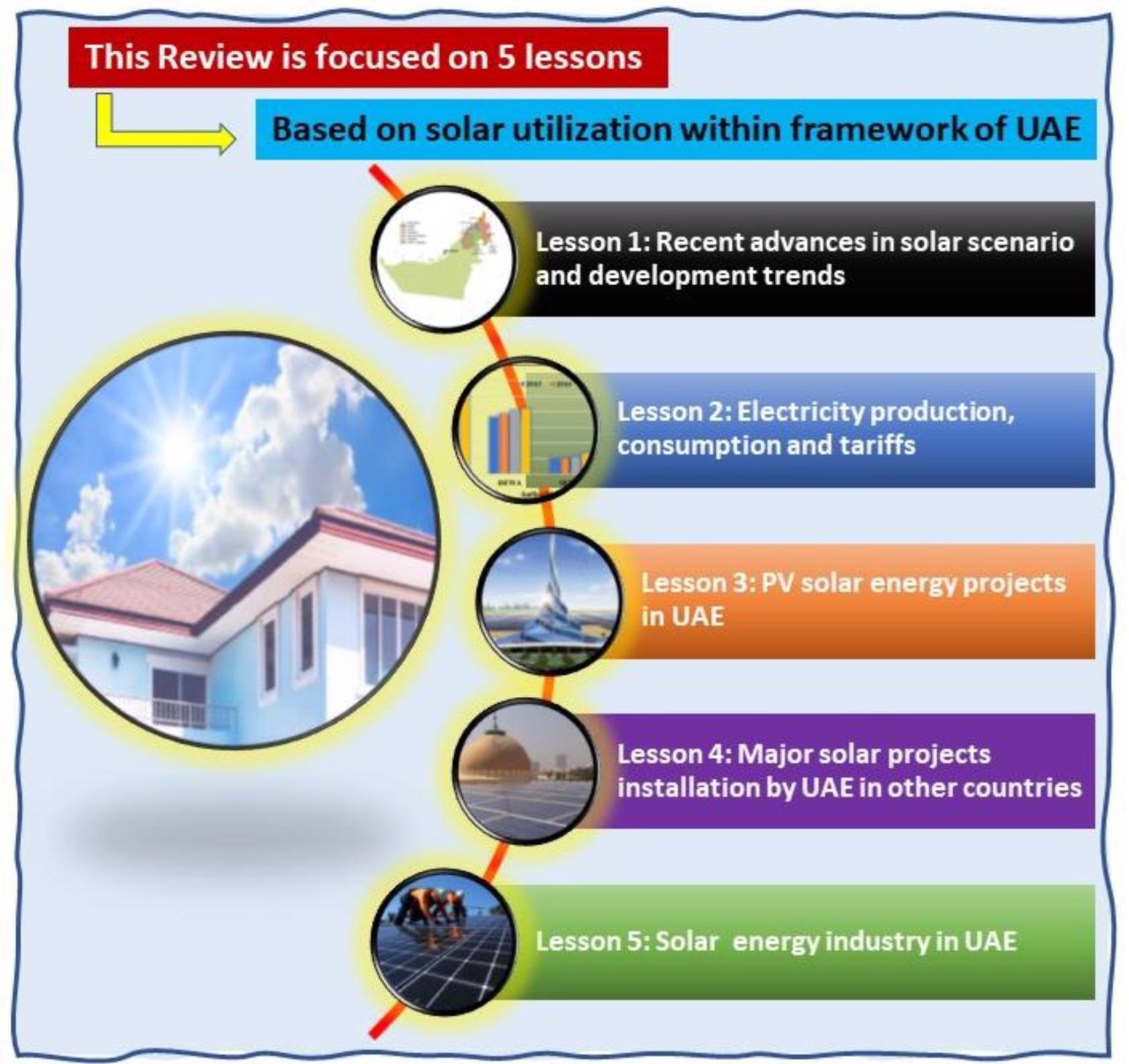
The layout of this review. Image Credit: Ramachandran, T et al., Energies
Observations
Desert covers 74% of the UAE's landmass. DuSol had a 50 MW annual capacity automated line for off-grid and on-grid modules, which was developed in partnership with Japanese and German equipment manufacturers. Masdar had constructed and deployed 7000 off-grid solar household PV systems in homes and commercial buildings in six remote regions: Matrouh, Al Wadi Al Jadeed, Qina, Sohag, Aswan, and Luxor.
The Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum solar project, with a total area of 77 km2 near Seih Al-Dahal, about 50 kilometers south of Dubai, was determined to be the world's largest solar park. The Department of Energy (DoE) had a gross generated electricity of 586,099 GWh, or 57.1%, followed by Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) with 352,951.95 GWh or 34.4%, Sharjah Electricity Water & Gas Authority (SEWGA) with 64,241.86 GWh or 6.3%, and Etihad Water and Electricity Authority (EWE) with 4405.14 GWh 2.4%. The energy industry was responsible for more than 90% of all greenhouse gas emissions in the UAE. From 100% in 1971, fossil fuel use was lowered to 99.81% in 2014.
The UAE government has taken a number of steps to increase the use of renewable energy sources, including solar, and the year 2030 has been set aside for PV. Solar energy progress in the UAE, however, faced numerous hurdles. There were issues with land use, backup capacity, and storage within the emirates. There were also concerns with dust and sand build-up on PV panels, as well as a lack of constancy in solar radiation.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study discussed several private solar enterprises operating in the UAE. These solar companies could be used for current or future solar projects in the UAE, assisting in the expansion of solar power capacity and environmental protection. Within the Gulf cooperation council (GCC) countries, the UAE has been a pioneer in renewable energy production, particularly solar. Photovoltaic, concentrated solar power (CSP), and other solar sources are available for the UAE. Because of the UAE's higher sun exposure, power can be generated to meet population growth demands while also lowering pollution, particularly CO2 emissions and other greenhouse gases.
The authors emphasized that more manufacturing enterprises are needed in all of the UAE's emirates. Another significant role is to increase awareness, share the experience through seminars and workshops, and provide scientific advice to UAE colleges, universities, and research organizations. Engineering programs need to change their curricula to include lessons on solar energy resources. They also believe that the UAE government must promote a varied energy mix in which electricity can be produced from all traditional energy sources, such as renewables, nuclear power, and coal power.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
Ramachandran, T., Mourad, A-H. I., Hamed, F., et al. A Review on Solar Energy Utilization and Projects: Development in and around the UAE. Energies 15(10) 3754 (2022). https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/10/3754