A team of researchers created a new polyoxometalate-based metal-organic complex, which they subsequently evaluated as a catalyst for the oxidation of different sulfides. They discovered that the complex has exceptional catalytic activity, reusability, and structural stability.
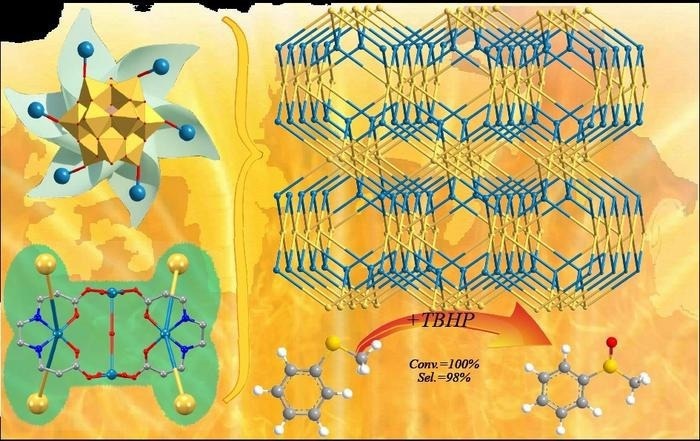
Each unit of the polyoxometalate (SiW12) joins with the copper (Cu4) complexes (top left) and each copper (Cu4) complex bridges the adjacent four (SiW12) units (bottom left) to create the novel 3D framework of CuW-EDDP. Image Credit: Polyoxometalates, Tsinghua University Press
On October 19th, 2023, the team’s study was published in the journal Polyoxometalates.
The selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides has been studied by scientists in a variety of domains. Sulfur and oxygen combine to form organic compounds called sulfoxides. These sulfoxides are highly valuable chemicals used in dyes, agrochemistry, medicines, and as chiral auxiliaries, which are crucial building blocks for the synthesis of extremely complex molecules.
The primary method used by scientists to create sulfoxides is the catalytic oxidation process of sulfides, which can be carried out in mild settings using homogeneous or heterogeneous catalysts and environmentally safe oxidants. Scientists are therefore intrigued by the prospect of creating a heterogeneous catalyst that is both highly effective and easily separated in catalytic oxidation reactions.
Polyoxometalates (POMs) are a type of nanomaterial with unique properties. High negative charges, remarkable redox ability, and organic grafting are among these characteristics. POMs have sparked a lot of interest in energy-related applications because of these characteristics. Material science, catalysis, medicine, environmental protection, and hydrogen production are all possible applications.
POMOCs, or POM-based metal-organic complexes, are an expanding subset of POMs. In addition to combining the best qualities of metal-organic complexes with POMs, POMOCs enhance POM aggregation, dissolution, and leaching. They have been applied in numerous fields, most notably catalysis.
To our knowledge, there are only a few reported POM-based metal-organic complexes with a 3D framework based on POM units and metal-organic complexes bridges, prompting us to investigate this rarely explored research field. Because copper-organic complexes possess intriguing architectures, topologies, and applications, design and synthesis of new POMOCs with 3D framework based on POMs and Cu-organic complexes is still challenging.
Zhong Zhang, College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Bohai University
The group obtained and described CuW-EDDP, a novel copper-incorporated POMOC, for this study. This POMOC is of the Keggin type. POMs’ structural shape is characterized by their Keggin-type. Two basic types of POM structures are the Keggin-type and the Dawson-type.
CuW-EDDP was synthesized by the team using hydrothermal conditions, which included heating in a stainless-steel reactor for three days, then cooling and drying. The group used thermogravimetry, elemental analysis, and infrared radiation spectra to examine the CuW-EDDP they had synthesized.
They found that the three-dimensional structure of the CuW-EDDP is distinct. They also discovered that CuW-EDDP can be employed as a heterogeneous catalyst to selectively oxidize different sulfides.
Based on previous studies, the group was aware that POMOCs that contained copper had demonstrated exceptional catalytic performance in a variety of oxidation processes, including the selective oxidation of sulfides.
This is so that the catalytic oxidation process can be aided by POMs and copper centers acting as catalytic active sites. CuW-EDDP’s many copper-active sites increase the catalyst's effectiveness.
The group investigated the ideal reaction parameters for the conversion of methyl phenyl sulfoxide into methyl phenyl sulfide through selective oxidation. They looked into the effects of solvent types, levels of tert-butyl hydroperoxide, CuW-EDDP doses, and reaction temperature. They conducted multiple control trials in which they oxidized methyl phenyl sulfide selectively to produce methyl phenyl sulfoxide.
Zhang added, “As an effective heterogeneous catalyst, CuW-EDDP exhibited excellent performance, good reusability and structural stability in the selective oxidation of methyl phenyl sulfide. It displayed high conversion (100%) and selectivity (98%) within 30 minutes.”
CuW-EDDP’s catalytic activity for the oxidation of various sulfide derivatives was also studied by the team.
With CuW-EDDP successfully synthesized, the team hopes that this work will serve as a guide for the development of new POMOCs based on Keggin- or Dawson-type POMs and metal-organic complexes with innovative topology and distinctive characteristics.
Jia-Yu Sun, Zi-Lan Wang, Zhong Zhang, Guo-Cheng Liu, and Xiu-Li Wang from Bohai University’s College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering in Jinzhou, China are among the research team members.
NSFC and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning province funded the study.
Journal Reference
Sun, J.-Y., et al. (2023) Hydrothermal synthesis, structure, and catalytic properties of a (4,6)-connected framework constructed from Keggin-type polyoxometalate units and tetranuclear copper complexes. Polyoxometalates. doi:10.26599/POM.2023.9140039
Article Revisions
- Jan 6 2025 - Meta Title and Description has been updated to fall inline with Google recommendations and a malformed link has been repaired.