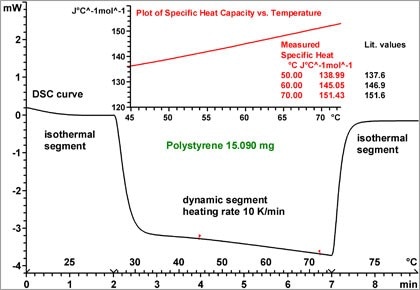
DSC is a measurement technique commonly used for the determination of specific heat capacity because of its ease of use, short measurement times and because it provides adequate accuracy.
The specific heat capacity is used to specify materials and is quoted in data sheets. It is important for improving technical processes such as injection molding, spray drying, and crystallization, and is an important property for the safety analysis of chemical processes and reactor construction.
Heat Capacity vs Specific Heat Capacity
The measured heat capacity depends on the sample size and does not characterize the material.
For DSC measurements, the heat capacity is essentially the ratio of the heat flow and the heating rate. The unit of the heat capacity, Cp, is Joules per Kelvin.
A more meaningful material property is the determination of specific heat capacity, cp. This is the heat capacity divided by the sample mass. The unit is Joules per gram Kelvin.
Cp Measurement Methods
This webinar presents six different methods included in METTLER TOLEDO's thermal analysis STARe software. The so-called Direct and Sapphire methods are performed using a conventional DSC instrument and a linear temperature program. The specific heat capacity can be also measured using different temperature-modulated DSC techniques, namely IsoStep DSC, Steady State ADSC, ADSC, and TOPEM.