In the webinar titled "Thermal Analysis of Composites", we describe a number of typical application examples that illustrate how thermal analysis can be used for the routine testing and development of modern composite materials based on polymers in various industry segments.
What is a Composite Material?
The term composite means that two or more constituent materials are combined together on a macroscopic scale to form a new material. The individual components remain separate and distinct within the finished composite material. The functional properties of the composite are however better than those of the individual constituents. For example, higher stiffness in a polymer is achieved by incorporating fibers into the polymer to reinforce it.
Industrial Applications
In many industries, composites are replacing metals because of their comparatively light weight, low price and better performance. Composites are widely used as high-performance engineering materials in the aerospace, aviation, automobile, building, electronics, sports-goods, and other industries.
Thermal Analysis of Composites
The most important effects that can be analyzed by DSC are melting behavior and the glass transition. DSC can also be used to determine the curing kinetics of matrix resins and influence of additives.
For TGA, the main applications are compositional analysis, for example filler and fiber content, and thermal stability.
TMA is normally used to study the expansion or shrinkage of materials and the glass transition.
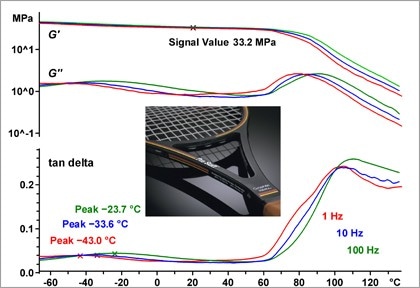
DMA is the most sensitive method for measuring the glass transition, modulus values, and the viscoelastic properties of materials as well as for investigating the influence of measurement frequency and displacement amplitude.