The integration of different sample viewpoints from various imaging modalities and scales is made possible by the ZEISS ZEN Connect software. The confluence of all imaging methods allows for the organization and overlay of images. The following are some of ZEN Connect’s key features:
- Overlay and align images from any source
- Shift to confocal, light or electron microscope and align one time
- Obtain an overall image
- Utilize overview image for navigation
- Save multi-modal data in well-ordered projects
An effective tool for a multi-user facility — for a materials researcher at a university or an industrial laboratory — ZEISS ZEN Connect is time-efficient, gives unique insights, and is effective.
Zen Connect enables the employment of several microscopy modalities or contrasting approaches, which is beneficial for complicated applications like testing additively built components, analyzing batteries for e-mobility, researching raw materials like oil, or even evaluating inclusions in metallic samples.
Highlights

Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
Overlay and Align All Images
- All image data in context can be aligned and displayed
- ZEISS ZEN Connect stores metadata for longer durations in such a way that external images can follow the well-established Bio-Formats standard
- Compatible with all third party imaging technologies
- Simple overview images or complex multi-dimensional images can be loaded from a mobile phone
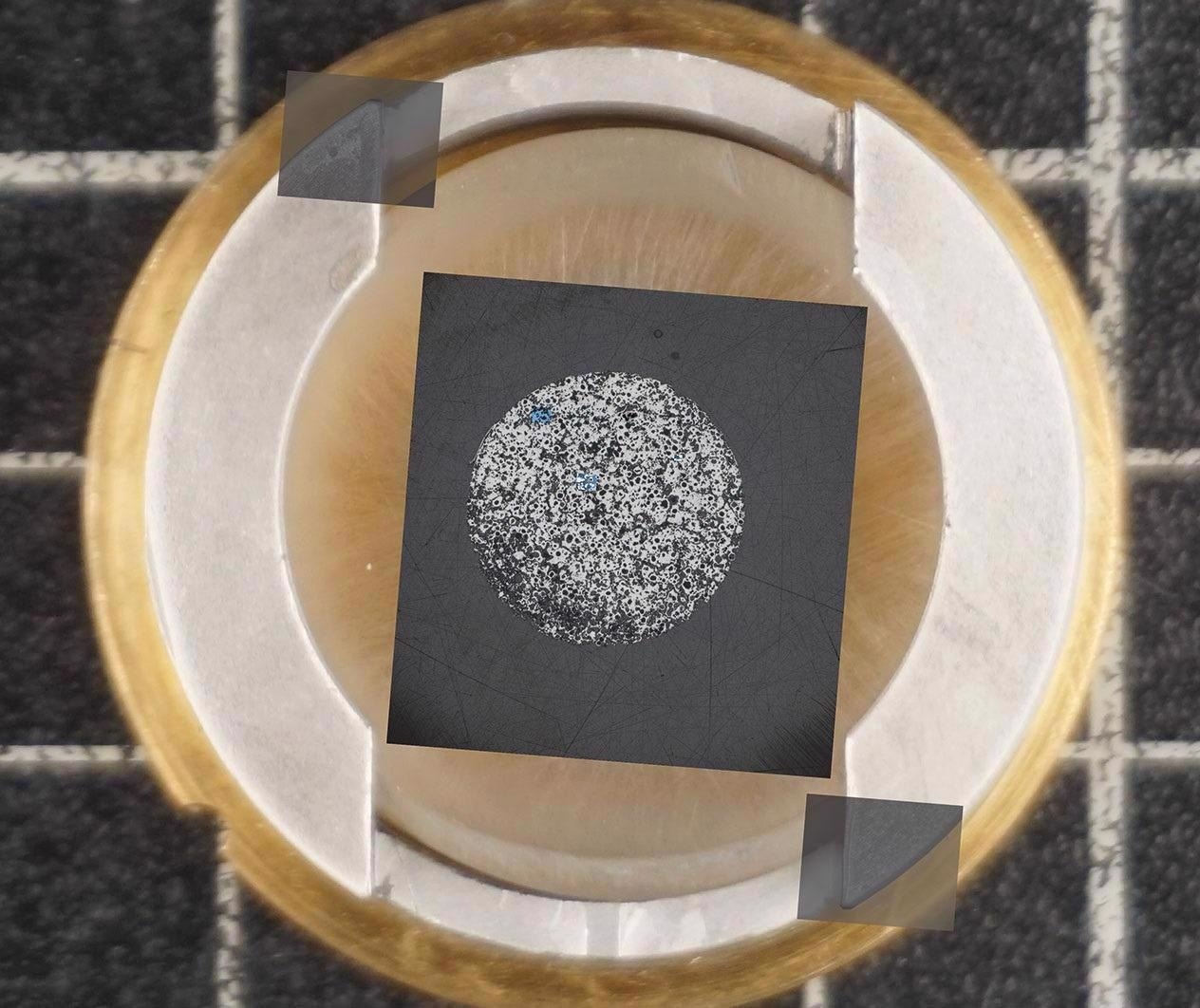

Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
Acquire Overview Images for Easy Navigation
- Adjust the stage to the right position with a click on the overview image and analyze ROIs
- Use overview images to route and find ROIs
- Identify succeeding images in context while zooming in and out through the borders of imaging technologies and resolution domains
- Mount the specimen on a sample holder from ZEISS or any third party
- Image the sample with any low magnification system or ZEISS stereo microscope
Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
Smart Data Management
- Obtain all the images and datasets associated with them
- Look for imaging parameters and microscope type using the filter function
- Stay informed about all the steps during the experiments or even months later
- An intuitive label is attached by default to every image once it is saved in the database projects
Applications
Material Research in e-Mobility
Permanent magnets will determine the future of e-mobility. To start with, get an overview picture, then use a Kerr microscope to observe the magnetic domains and identify trustworthy magnetic phases. The next phases would reveal further details by increasing resolution from micrometer to nanometer scales.
Users may draw inferences and connect magnetic parameters and sample morphology based on these findings. It is preferable to assess data in a broader context with the highest resolution.

Large-scale overview, acquired with ZEISS Axio Imager. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
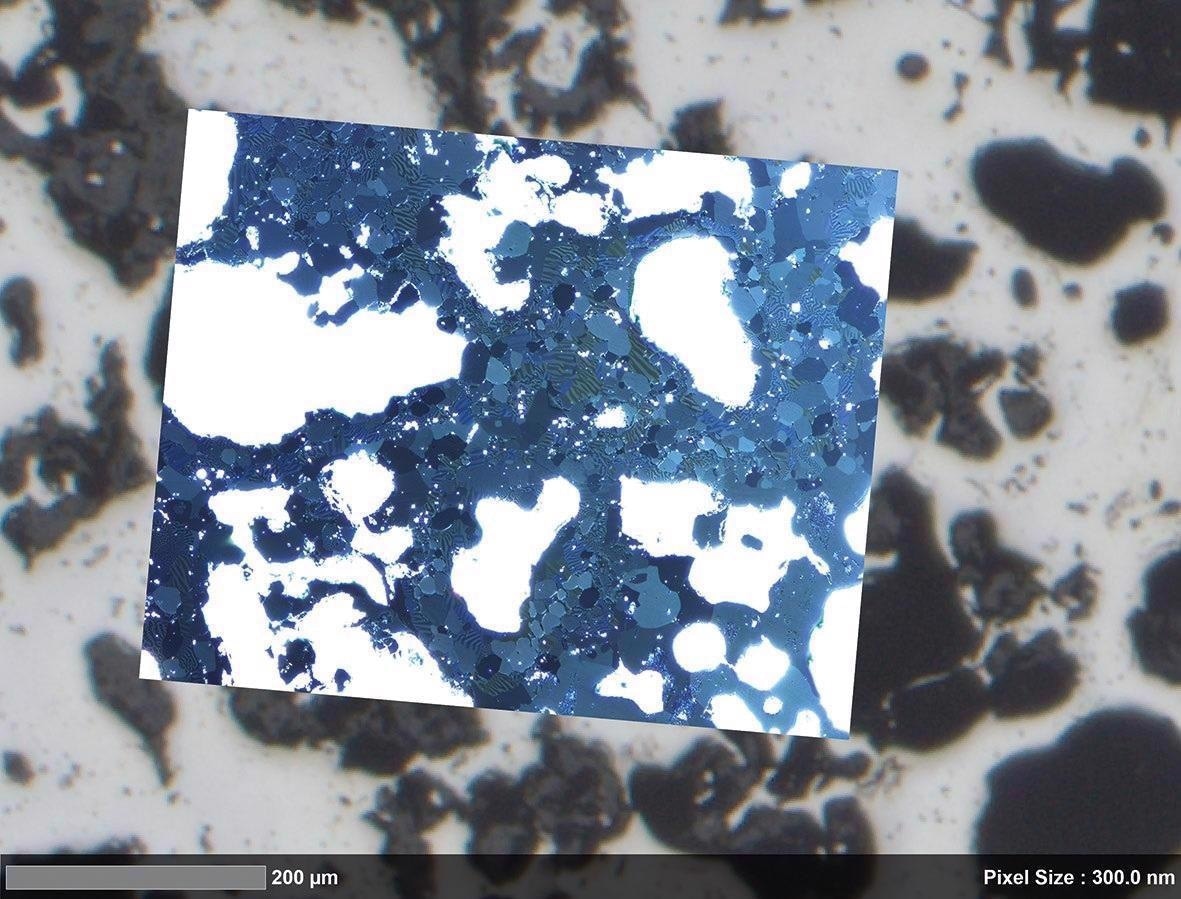
Magnetic domain structure visualized by Kerr microscopy. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
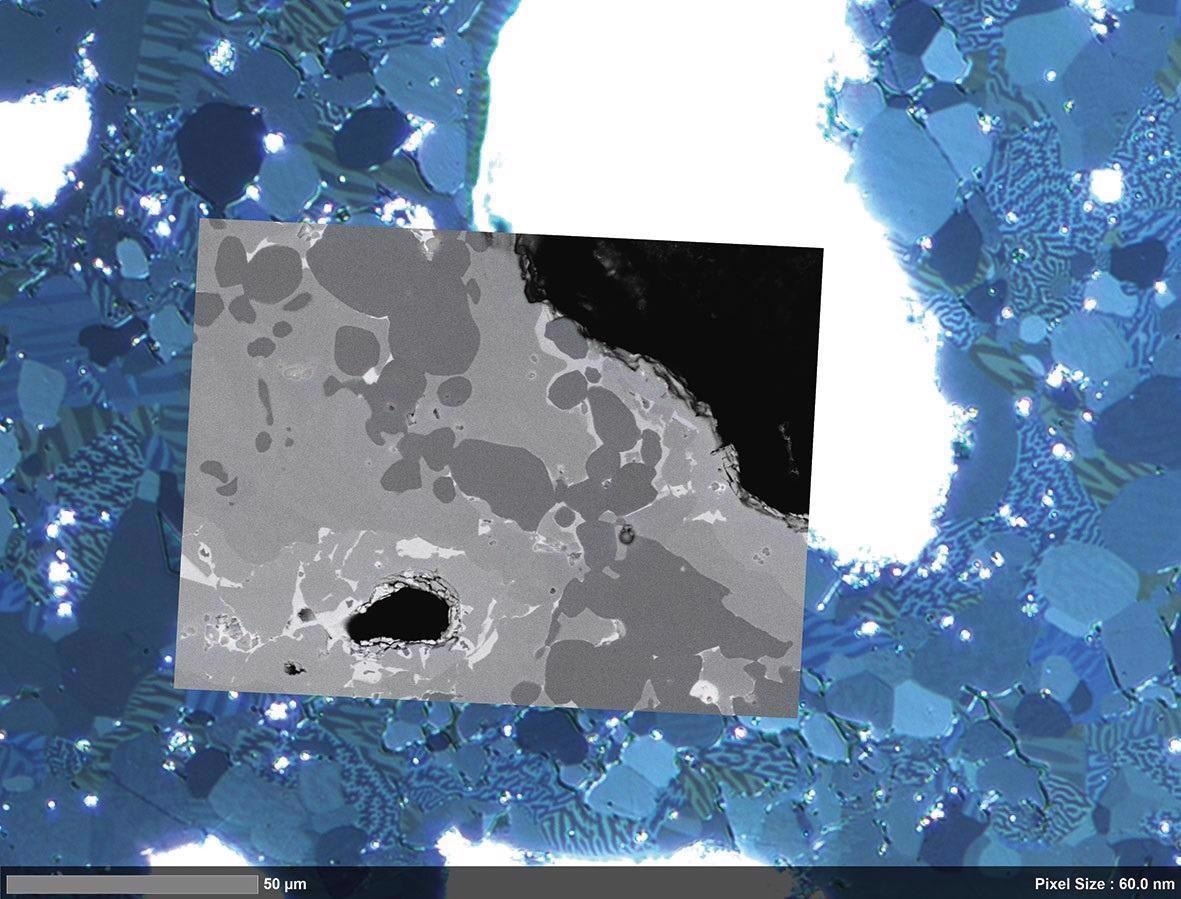
Correlated high-resolution image acquired with ZEISS Sigma 300 VP. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
Material Research Oil Recovery, Nuclear Waste Disposal and Carbon Capture and Storage
Investigate the pore architecture of carbonate rocks. Define flow, reaction, and transport at different length scales and with different structural heterogeneity. For a clearer view, use automated light microscopy.
ZEISS ZEN Intellesis can be used to categorize macrostructures and detect pore structures, microporous grains, and solid rock grains using distinct colors, textures, and intensities. Using the provided data, regions of high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscopy may be identified. The variation in nanometer-scale pore structure may be observed in the context of macroscopic heterogeneity.
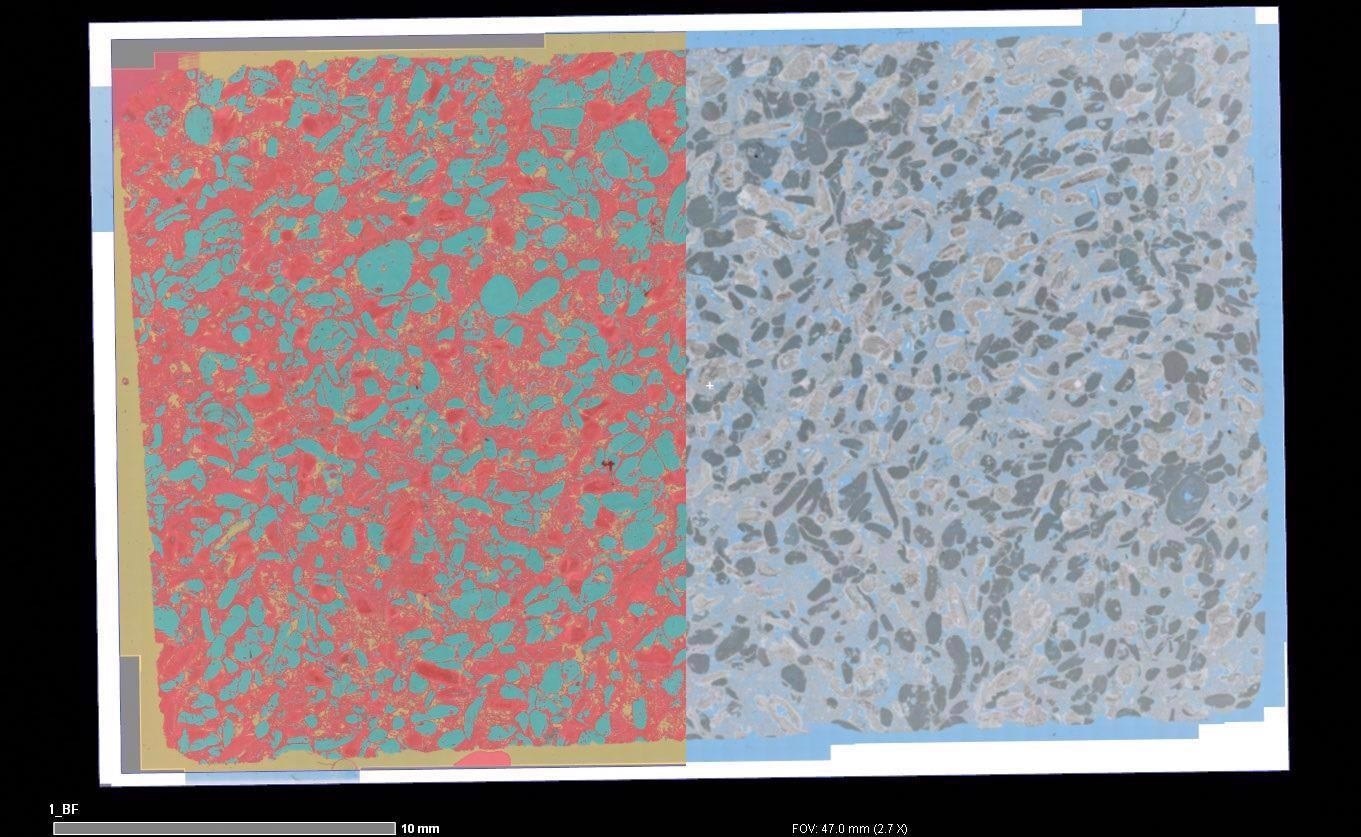
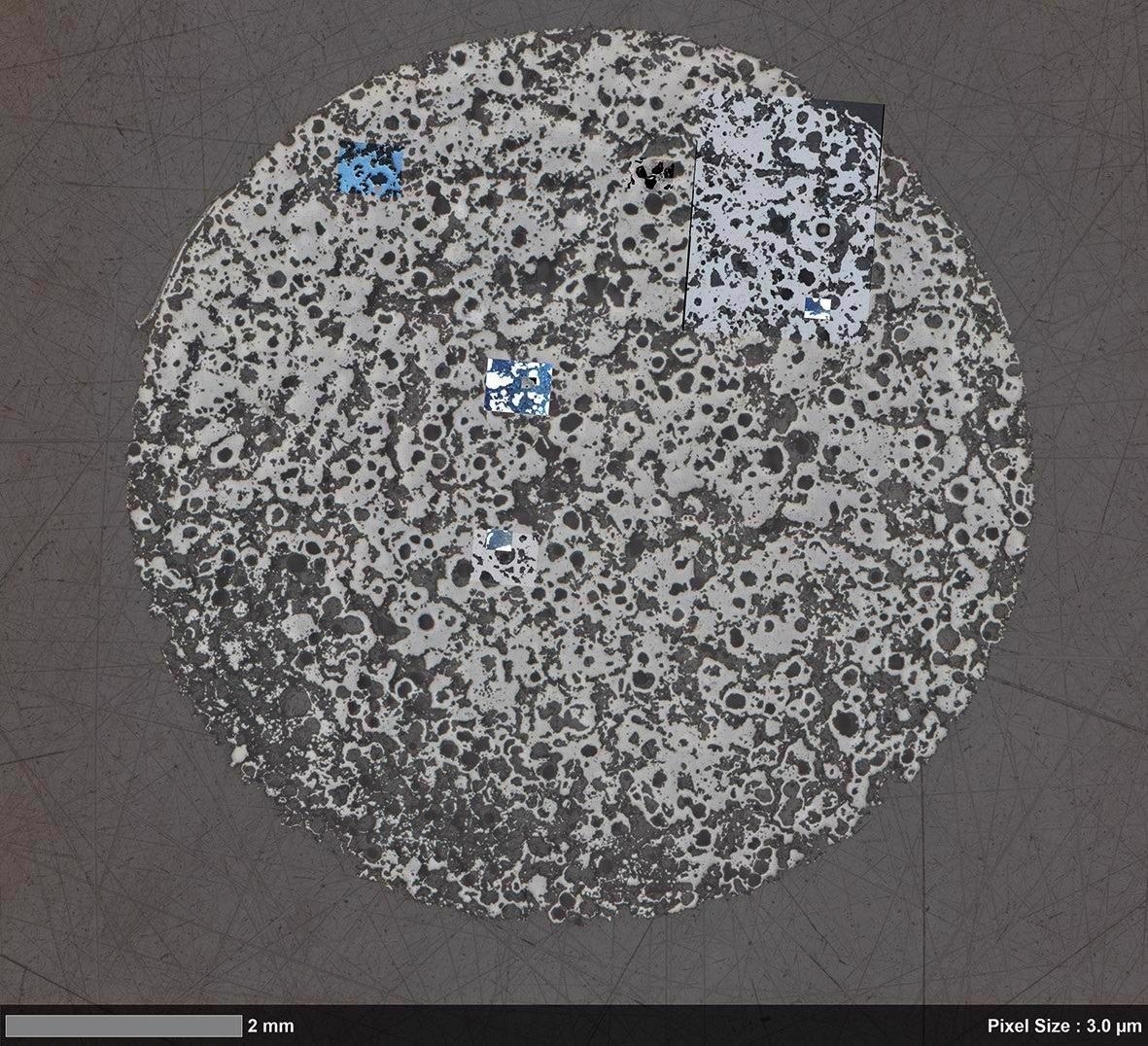
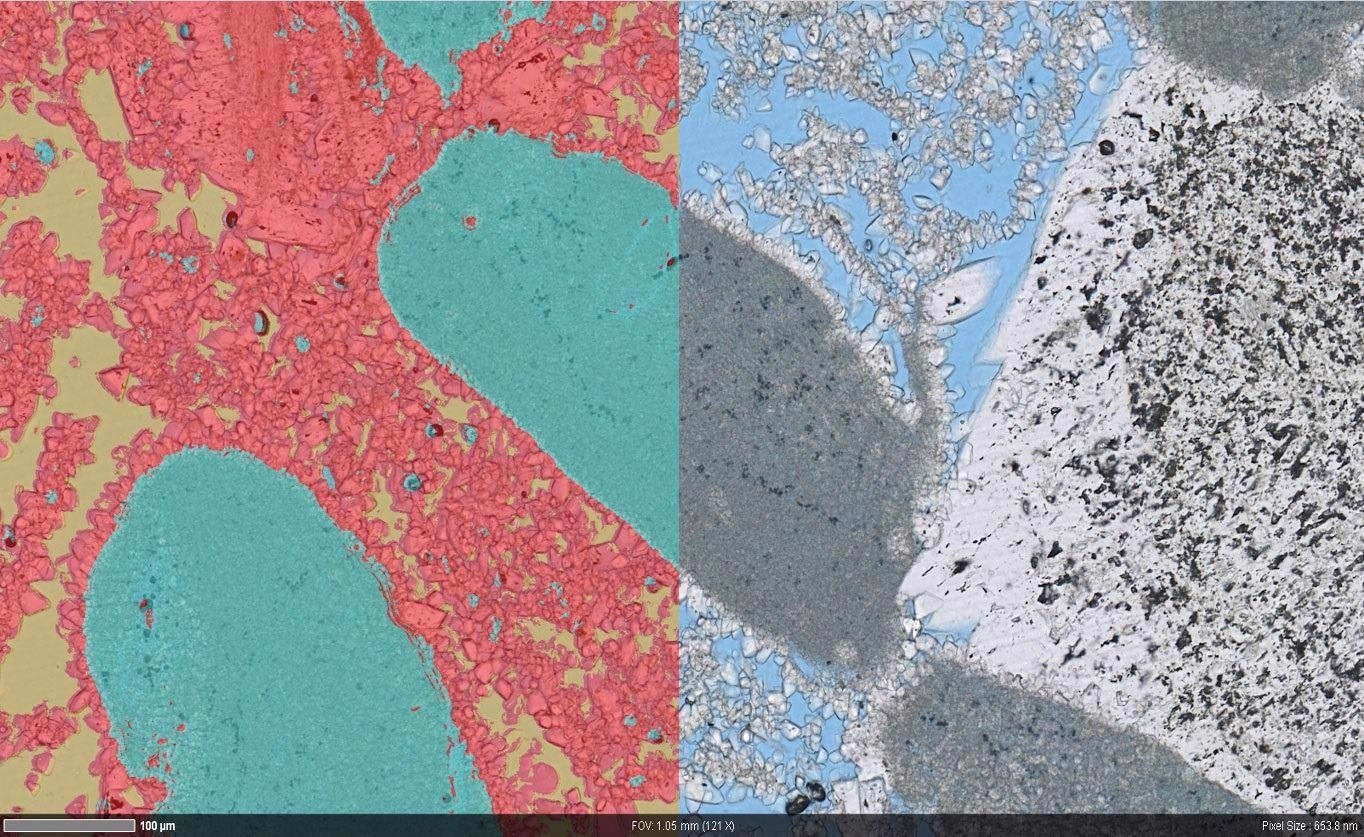
Overlay of macroscopic segmentation (left) and automated light microscopy image (right) showing the microporosity and microporous grains. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
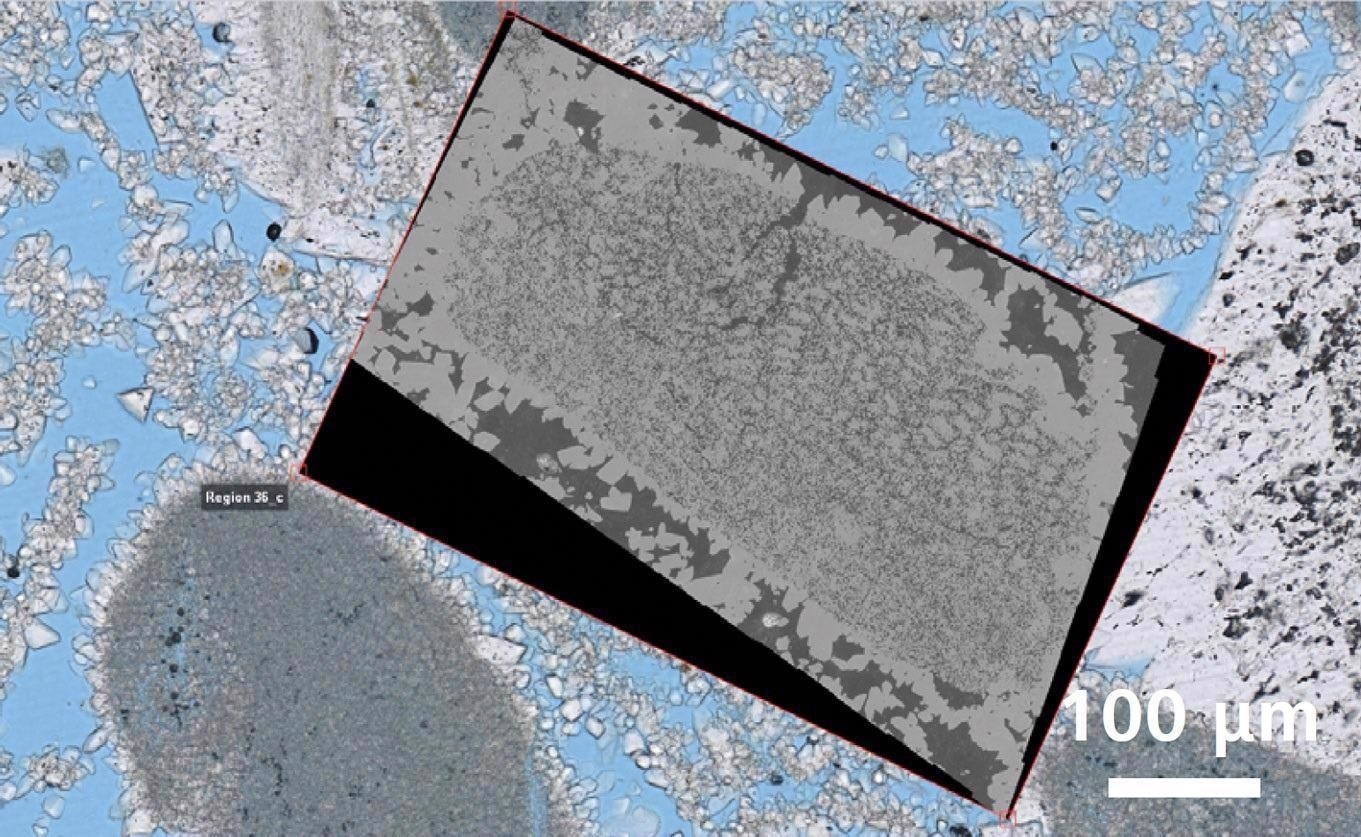
Correlative overlay of high-resolution light microscopy data and nano-scale electron microscopy data. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
Overlay of segmented (left) high resolution light microscopy data (right) showing the pore structure in more detail. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
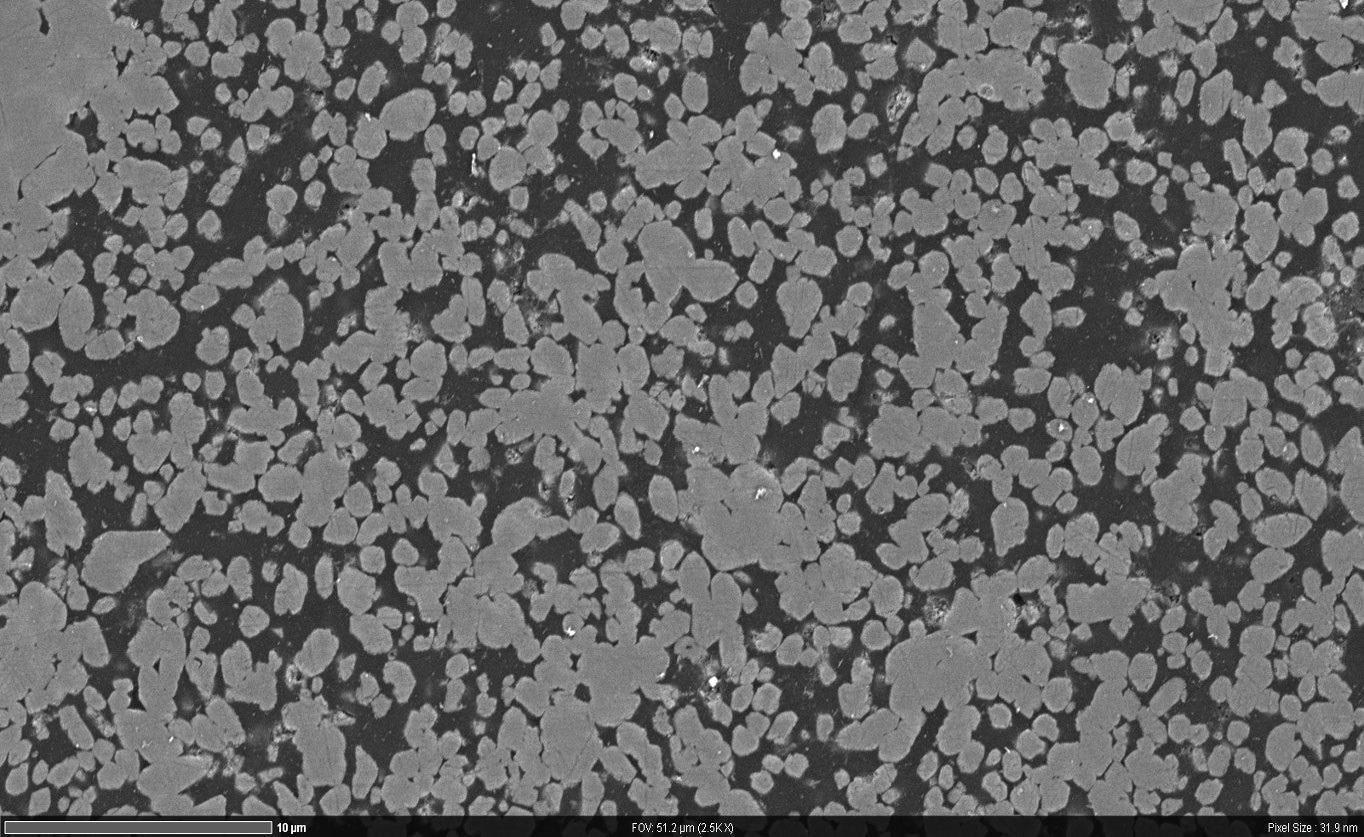
High resolution nano-scale microscope data. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
Material Research on Inclusions in Calcium-Treated Steel
The calcium treatment of steel helps limit the production of harmful manganese sulfide (MnS). This may cause elongation and, as a result, anisotropy in the steel during rolling.
When modified MnS is utilized, tougher calcium sulfide (CaS) is generated, which aids in the preservation of steel isotropy. Join the two photos together to get a large-scale perspective of the complete sample. A high-resolution picture may be obtained using SEM. To identify the precise location of EDS analysis, change locations.
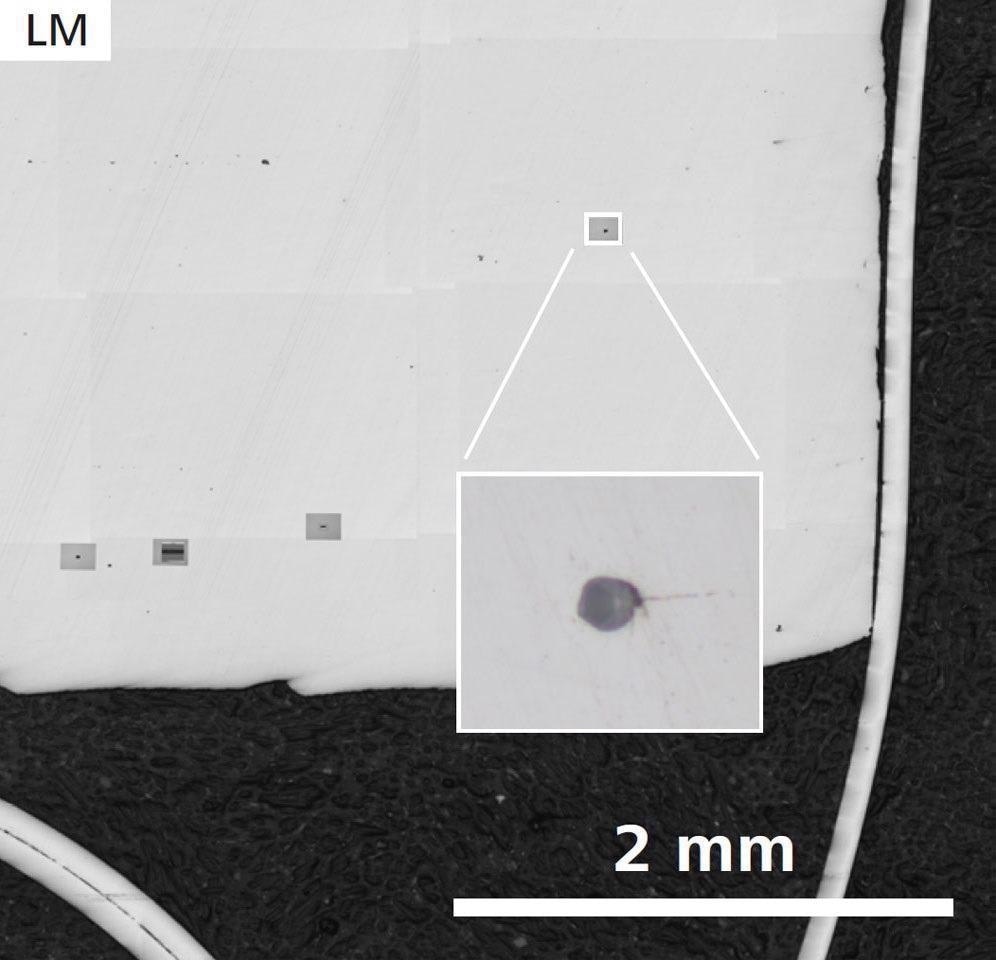
First sample, without Ca treatment: Sample Overview and detail of one inclusion (inset) acquired by ZEISS Axio Observer. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
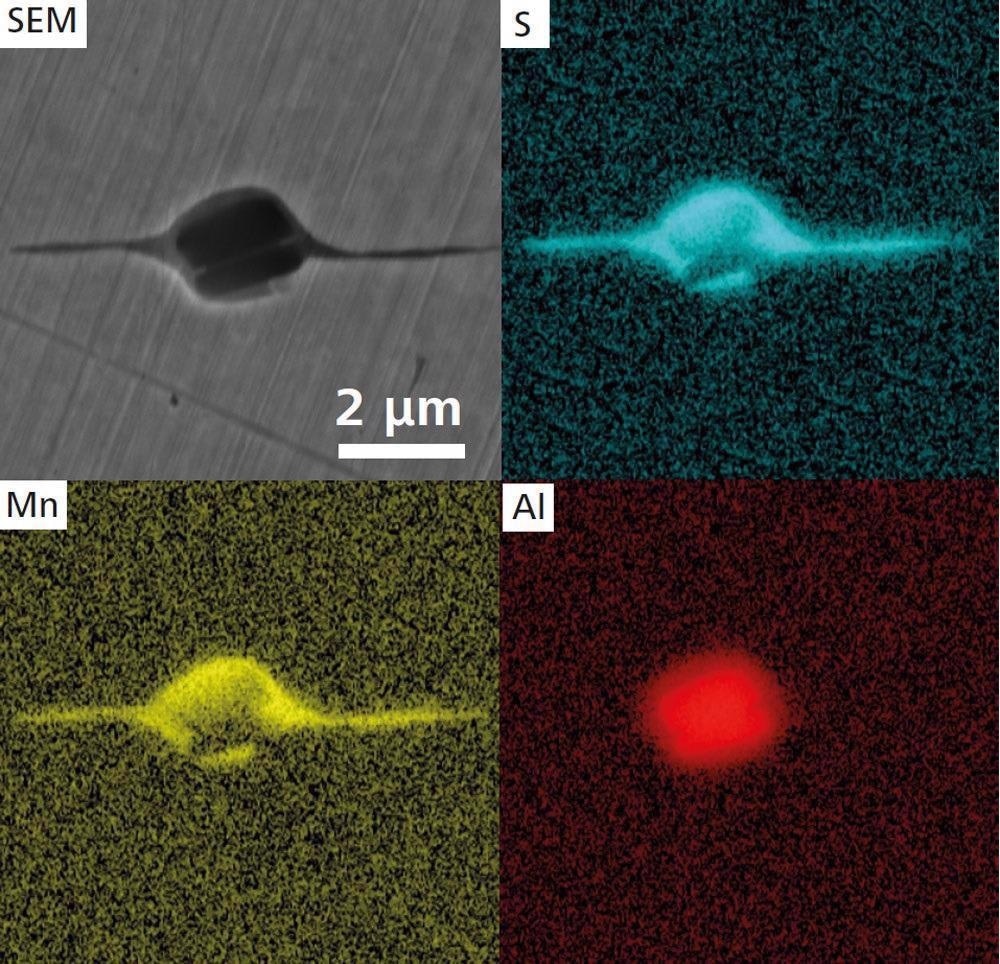
Higher magnification SEM image (ZEISS Crossbeam 550) and EDS maps of an elongated MnS inclusion. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
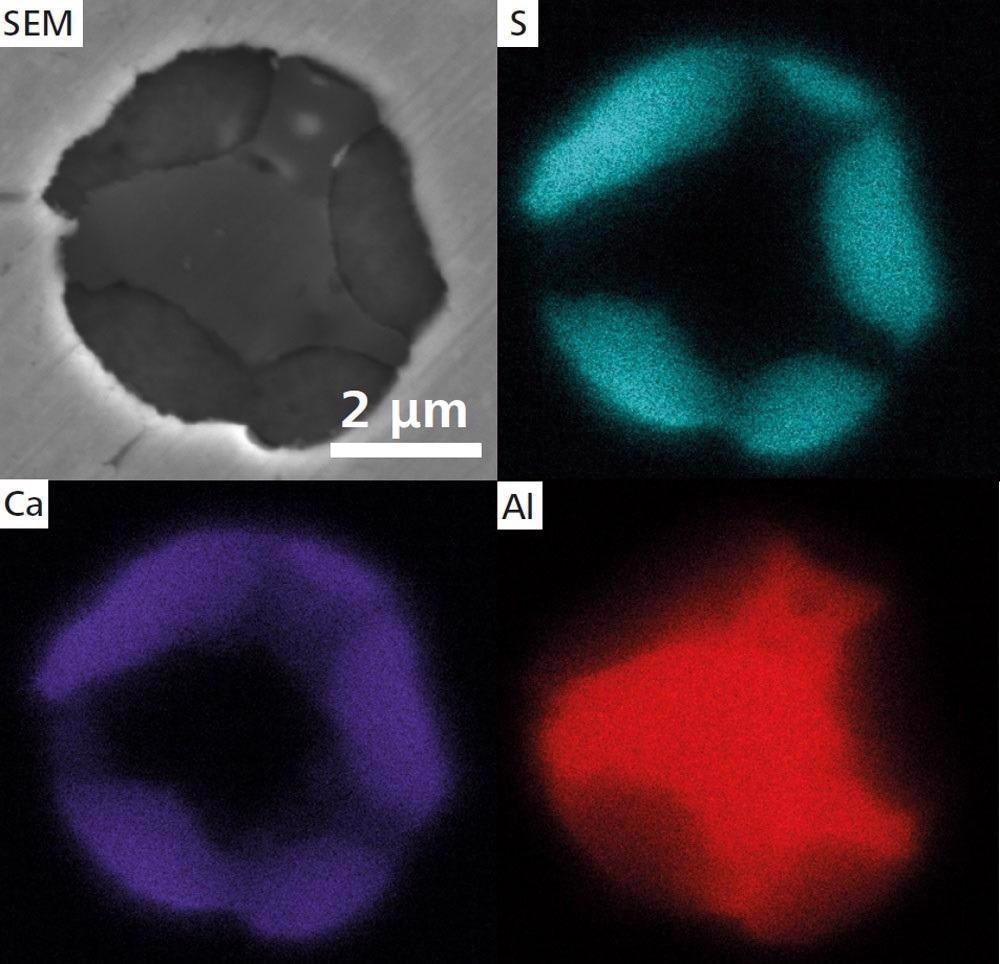
Second sample with Ca treatment SEM image of a globular CaS inclusion and EDS maps. Image Credit: T. Schubert, Aalen University, Germany
Accessories
ZEISS ZEN Data Storage
ZEN ZEISS Data is linked to a central data management system in the laboratory. It allows for data gathering after post-capture operations and the preservation of individual pictures. The sharing features and data access are available to all participants.
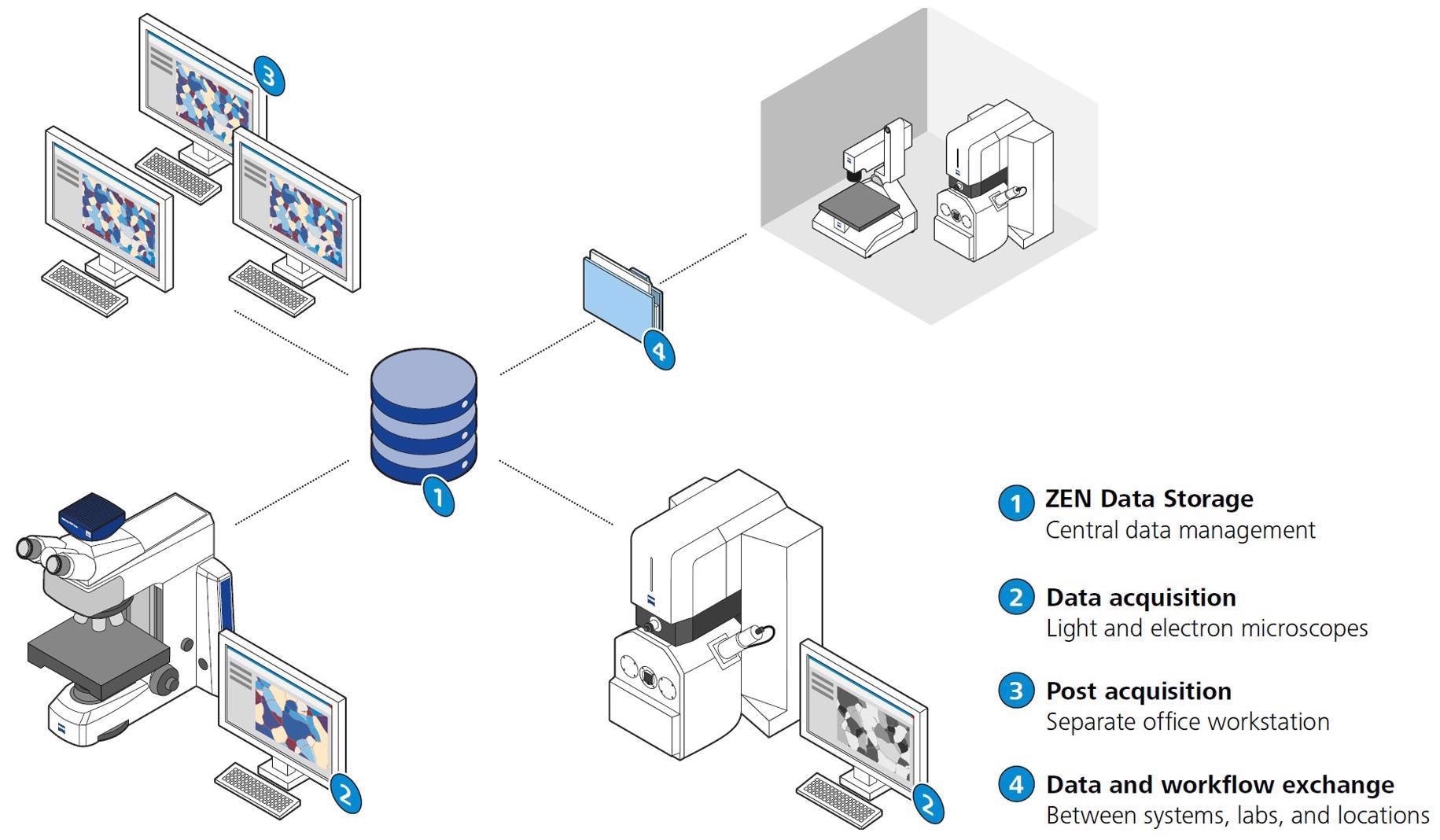
Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
ZEISS Shuttle and Find for Correlative Microscopy
The ZEISS Shuttle & Find software module is simple to use and provides an efficient process for overlaying data from scanning electron microscopes and light microscopes.
A specimen container with fiducial markers may be used to build a coordinate system in seconds. The light microscope may be used to designate regions of interest in the material. To get access to high-resolution imaging and analytics, change the ROIs in the electron microscope. Finally, connect the photos collected with various microscopical procedures.
Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
Image Segmentation in Microscopy
Deep learning benefits are utilized to efficiently separate photos and get access to real-world data. The pivot for all subsequent image analysis procedures is image segmentation.
ZEISS ZEN Intellesis uses deep learning and Python to get repeatable segmentation results. Even inexperienced users can use the program, and the software module will automatically segment photos. As a result, it saves time and decreases user bias.
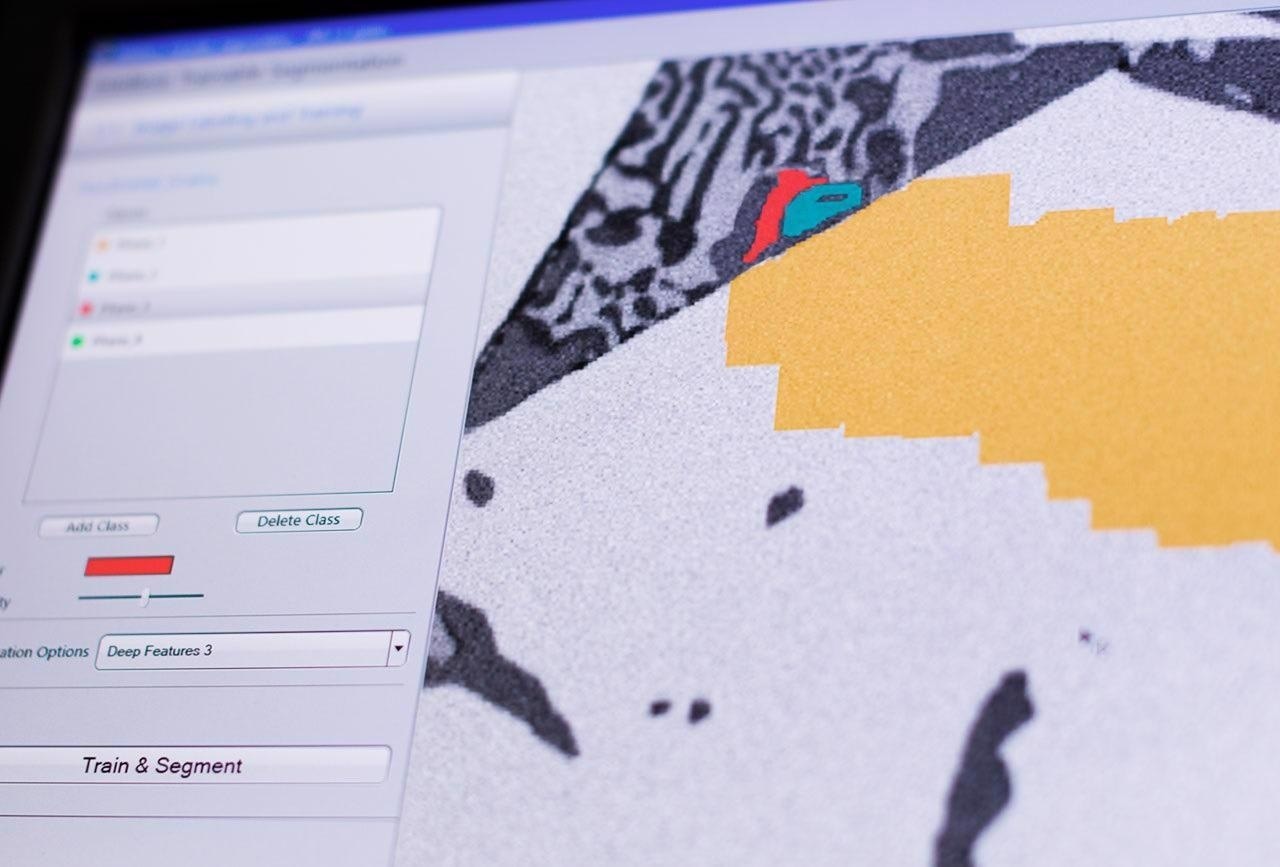

Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials