The battery system of Aluminum-sulfur (Al-S) exhibits a theoretical energy density as high as 1340 Wh kg-1. Such high energy density and affordable raw materials are the reasons behind making the Al-S battery a hopeful alternative-energy storage device.
 After mixing the Na2S4 solution and the delaminated Ti3C2Tx suspension evenly, HCOOH solution was added slowly, then nano sulfur was formed in-situ on the delaminated Ti3C2Tx flakes. Image Credit: ©Science China Press.
After mixing the Na2S4 solution and the delaminated Ti3C2Tx suspension evenly, HCOOH solution was added slowly, then nano sulfur was formed in-situ on the delaminated Ti3C2Tx flakes. Image Credit: ©Science China Press.
But sulfur is a conversion-type cathode material and will produce a range of sulfides and polysulfides during the charge or discharge process. Polysulfides are prone to losing electrical contact with the host and dispersing to the electrolyte or anode, resulting in the shuttle effect.
This is considered to be the primary reason for low efficiency, low capacity and quick capacity decay. Consequently, structural design strategies and novel electrode materials are preferred to overcome such obstacles.
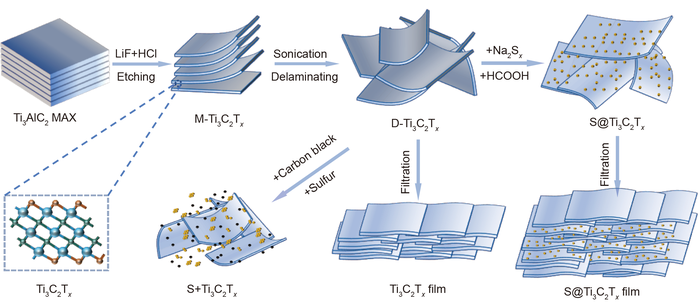
Scientists from Shanghai Jiao Tong University have developed a new binder-free S@Ti3C2Tx sandwich structure film with even sulfur dispersion as a high-capacity cathode, offering various significant benefits.
This new structure includes three parts. The film’s lower and upper surfaces were covered with a very thin pure Ti3C2Tx film, and the main part in the middle was made of a S@Ti3C2Tx composite. The composite was developed by the in-situ controllable chemical deposition of nano sulfur present in the Ti3C2Tx solution. This guaranteed the dispersion of sulfur.
The main attraction of this material is that the protective layer was directly added on the surface of the S@Ti3C2Tx composite to block the polysulfides, different from the previously reported strategy of using graphene coating on the separator to mitigate the shuttle effect.
Xiao Zheng, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Usually, the polymer binder is known as an inactive component that has the ability to increase the electrode mass and decrease the battery’s energy, thereby easily experiencing side reactions with ionic liquids.
It is enough to just filter and dry the binder-free film - no conductive agents, extra binders or poisonous organic solvents were required in the preparation process. Ti3C2Tx had the function of a binder and also a conductive agent.
Additionally, Xiao Zheng and Zhilong Wang utilized density functional theory (DFT) calculations to forecast the adsorption of polysulfides on Ti3C2Tx and made use of common graphene materials as a reference to emphasize the benefits of Ti3C2Tx. Later, the researchers suggested the Al-S batteries’ reasonable discharge-charge reaction mechanism.
Consequently, their electrode displayed outstanding cycling performance. The initial reversible capacity of 489 mA h g-1 at 300 mA g-1 after the initial short-term activation, and the capacity stayed at 415 mA h g-1 following 280 stable cycles. This has an average Coulombic efficiency of approximately 95%.
Journal Reference:
Zheng, X., et al. (2022) Binder-free S@Ti3C2Tx sandwich structure film as a high-capacity cathode for a stable aluminum-sulfur battery. Science China Materials. doi.org/10.1007/s40843-021-1913-4.