Experience the new LaserFIB for ZEISS Crossbeam, the femtosecond laser for ultrafast large-sample material processing for huge samples. Fabricate samples of a size of 10 μm to 1 mm or larger. Cut a deep cross-section through a hard material like SiC to directly reveal the structures of interest.
As the laser is coupled to a specialized chamber that is distinct from the main instrument chamber, users can easily avoid contamination of the FIB-SEM while laser milling.
Users get the following advantages with the innovative LaserFIB for ZEISS Crossbeam:
- Massive material removal: In a matter of minutes (up to 15 moi. µm³/s) prepare extremely huge cross-sections, up to millimeters in width and depth.
- Combining laser and FIB: Gain quick access to deeply buried structures for focussed ion beam scanning electron microscope (FIB-SEM) investigation and further FIB machining.
- Minimal damage: Damage and heat impacted zones are kept to a minimum thanks to ultrashort laser pulses (femtosecond laser) in a specialized chamber — with no instrument contamination.
Massive Material Removal
Prepare Larger Samples in Less Time
The new LaserFIB for ZEISS Crossbeam is a perfect instrument for preparing exceptionally large cross-sections in minutes, up to millimeters in width and depth. LaserFIB achieves the greatest removal rates of up to 15 moi. µm³/s because of the ultrashort pulse length of the femtosecond laser.
These high ablation rates are suitable for preparing samples for further FIB machining with ZEISS Crossbeam, which complements LaserFIB with even greater accuracy on a smaller scale (100 nm – a few 10 μm).
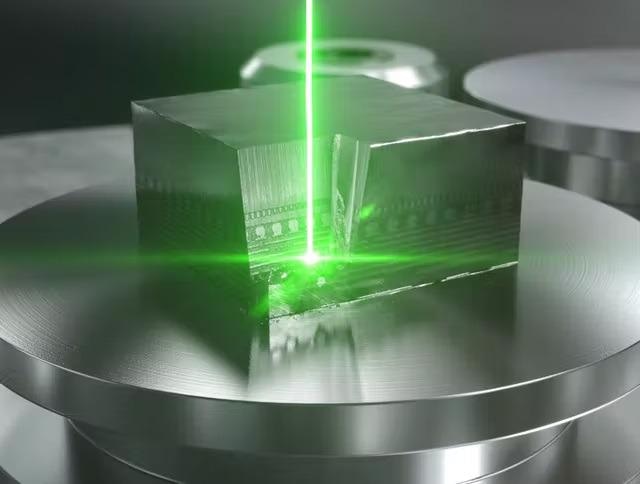
Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH
Combining Laser and FIB
Reveal All Structural Details
Directly expose regions covered beneath the surface, displaying all structural features in a variety of materials. Whether users are working with a hard or soft substance, a conducting or insulating material, LaserFIB can process it at a faster rate. Preparation of titanium alloy pillars for micromechanical testing or tungsten carbide cube preparation are examples of applications.
Users may correlate the FIB-SEM reference picture with 3D data, such as X-Ray microscopy data, before laser processing. Return the sample to the main FIB-SEM chamber for examination after laser processing. Finish with FIB polishing to bring out even more highlights.
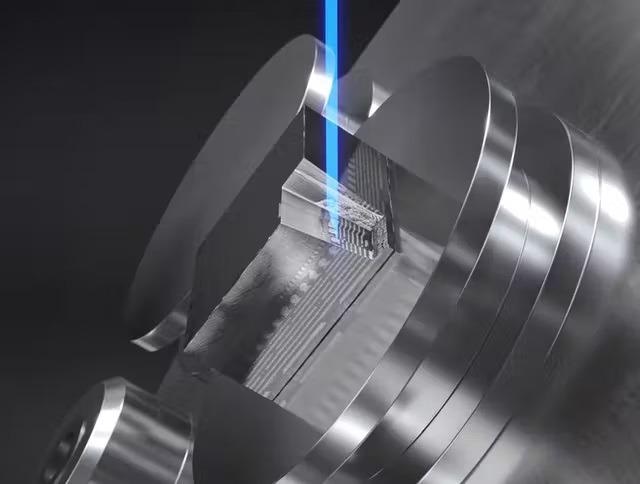

Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH
Minimal Damage
Conduct Quasi-Athermal Ablation
LaserFIB uses ultrashort laser pulses (femtosecond laser) to perform quasi-athermal ablation, which minimizes sample damage and heat impacted zones.
To eliminate contamination and permit safe and quick sample movement between the laser chamber and the main FIB-SEM chamber, the laser work is done in a separate chamber.
Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH