With the help of energy-dispersive X-Ray spectroscopy (EDS) maps and tomographic image series (obtained by TEM, STEM, or scanning TEM), Thermo Scientific Inspect 3D Software offers an easy-to-use solution for aligning the data and creating a 3D reconstruction.
Inspect 3D Software provides basic visualization features. With Inspects 3D Software, all Thermo Scientific TEM, STEM, and EDS tomography software is fully compatible.
An initial coarse X-Y alignment based on image cross-correlation is performed by Inspect 3D Software. Patch tracking or automated bead tracking techniques can further improve alignment.
Bead tracking adjusts rotation and magnification variations for every picture by following several spherical particles on the specimen throughout the tilt series. Throughout the tilt series, patch tracking monitors different regions of the image and then combines the results.
Weighted back projection (WBP) and simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique (SIRT) are the two traditional algorithms for 3D volume reconstruction that Inspect 3D Software provides.
Inspect 3D Software provides simple EDS-tomography reconstruction, known as HAADF-EDS bimodal tomography (HEBT), resulting in improved elemental reconstruction by simultaneously processing STEM and EDS files.
Iterative reconstruction techniques offered with Inspect 3D Software include;
- Simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique (SART)
- Conjugate gradient least squares (CGLS)
- Expectation maximization (EM), in which elongation artifacts are significantly reduced when compared to SIRT reconstruction
The resulting reconstructed volumes can be directly imported into Thermo Scientific Avizo and Amira Software for further visualization and analysis.
Key Features
Tomography post-alignment and reconstruction module. Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific – Electron Microscopy Solutions
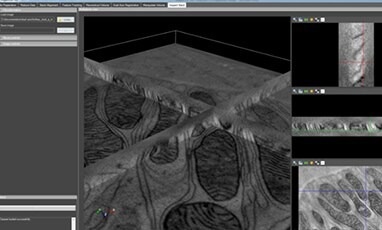
Inspect 3D reconstructed 3D volume screen capture. Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific – Electron Microscopy Solutions
- Utilizing the simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique maintains complete spatial information and improves the signal-to-noise ratio during reconstruction.
- Feature tracking can incorporate artificial features such as gold markers or recognizable intrinsic specimen features for image alignment.
- Bead cloaking involves the removal of gold beads from the image data post-alignment to prevent their appearance in the final reconstruction.
- The algebraic reconstruction technique employs iterative comparisons of reconstruction projections to original projections, adjusting the reconstruction to minimize disparities.
- Cross-correlation, devoid of markers, benefits from an array of filters and image-processing tools to enhance the alignment process.